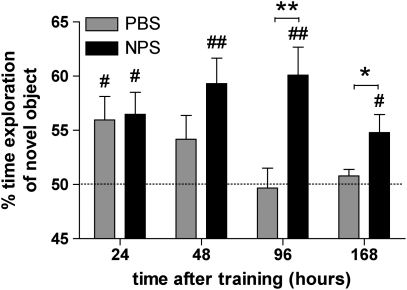
Figure 4.
Neuropeptide S (NPS) enhances novel object recognition. Mice were trained with objects A and B for 5 min and then injected with vehicle or 1 nmol NPS 5 min after training. After 24, 48, 96, or 168 h, mice explored one familiar and one novel object. NPS-injected mice spent more time exploring the novel object at longer test delays. Separate groups of mice were used for each time point. Numbers of animals at 24, 48, 96, and 168 h delays: phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), n=7, 7, 8, and 8, respectively; NPS, n=7, 8, 8, and 8, respectively. **p<0.01, *p<0.05, two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Bonferroni's post hoc test. #p< 0.05, ##p<0.01, one-sample t-test compared with 50% chance level. The dashed line indicates 50% exploration time if none of the objects is preferred.