Figure 1.
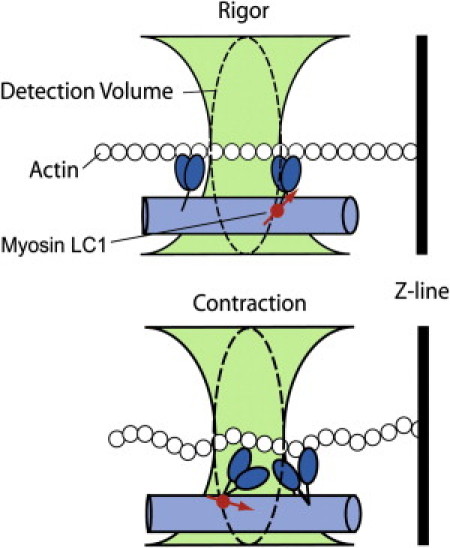
Origin of fluorescence fluctuations. A small fraction of myosin within the myofibril is bound to rhodamine-labeled LC1 (red circle). In rigor (top panel) there are no fluctuations in the orientation of the fluorophore's transition dipole (red arrow). During contraction (bottom panel) the myosin cross-bridges are cycling, which changes the orientation of the rhodamine's transition dipole and causes fluctuations of polarized intensity. We measure fluctuations in dipole orientation by recording parallel (‖) and perpendicular (⊥) components of the emitted fluorescent intensity by the cross-bridge-bound fluorophores.
