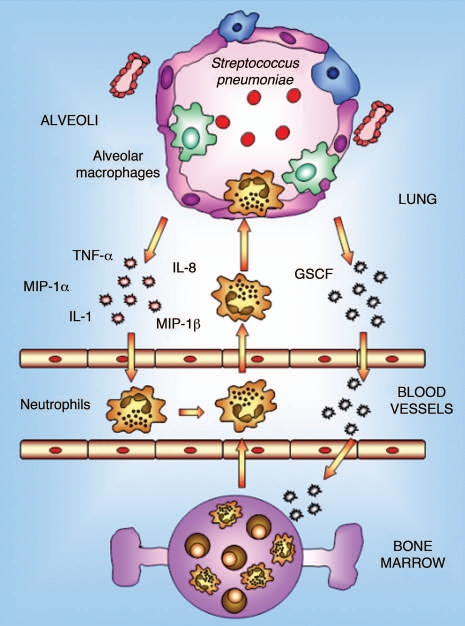
Figure 1.
Innate immune response in lung. Alveolar macrophages constitute the first line of phagocytic defense against infectious agents and play a prominent role in lung immunity by initiating inflammation and immune responses. In the event that invading pathogens are too virulent or represent too large a load to be contained by macrophages alone, alveolar macrophages are capable of generating mediators that orchestrate the recruitment of large numbers of neutrophils from the pulmonary vasculature into the alveolar space. These neutrophils provide auxiliary phagocytic capacities that play a critical role in host defense against pathogens.