Figure 5.
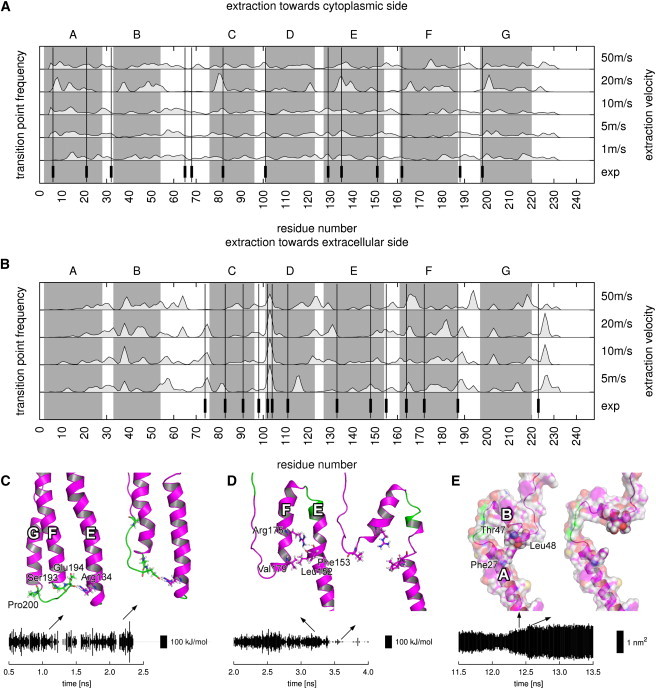
(A and B) Comparison between AFM anchor points (vertical bars and lines) (28) and frequency of transition points determined by MD (light gray areas). Transition point histograms are filtered with a Gaussian filter with a one residue half width. (Dark gray areas) Helices. (C–E) Structural and energetic determinants of anchor points. Each panel shows snapshots before and after rupture of an anchor point. The plots show hydrogen bond energies (C and D) or hydrophobic solvent-accessible surface areas (E) of selected residues. Bold letters denote helices. Key residues are shown as sticks (C and D) or spheres (E). (C) Anchor point Pro200 in a stable conformation and shortly before rupture. The plot shows the summed energy of hydrogen bonds between Arg134 and Ser193 and Glu194. (D) Anchor point Val179 before and after rupture. The plot shows the summed energy of hydrogen bonds belonging to Arg175. (E) Anchor point Leu48 before and after rupture. The plot shows the hydrophobic solvent accessible surface area of Phe27.
