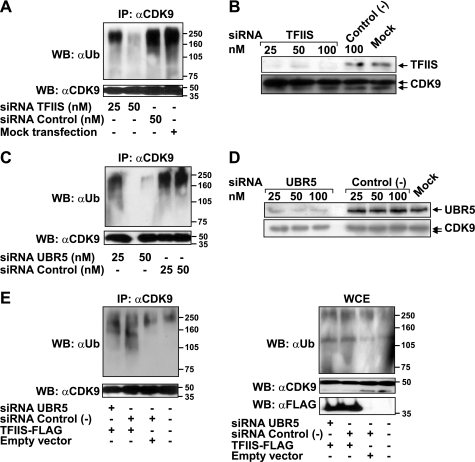
FIGURE 4.
TFIIS or UBR5 knockdown decreases the ubiquitination of CDK9 in vivo, and UBR5 is required for the effect of TFIIS on this ubiquitination event. A, HeLa cells were transfected with the indicated concentrations of siRNAs targeting TFIIS or control nontargeting siRNAs or mock transfected. The cells were treated with lactacystin and lysed, and the lysate was used in immunoprecipitation experiments with an anti-CDK9 antibody (C20). The eluates were run on SDS gels and immunoblotted with anti-ubiquitin or anti-CDK9 antibodies. B, comparison of knockdown efficiencies resulting from treatment with siRNAs targeting TFIIS or control nontargeting siRNAs. C, HeLa cells treated with the indicated concentrations of siRNAs targeting UBR5 or nontargeting siRNAs were assayed for in vivo ubiquitination (as in A). D, comparison of knockdown efficiencies resulting from treatment with siRNAs targeting UBR5 or control nontargeting siRNAs. E, HeLa cells treated with siRNAs targeting UBR5 or nontargeting siRNAs (50 nm) or mock-treated were transfected with a construct driving the expression of TFIIS-FLAG or with an empty vector. An in vivo ubiquitination assay (as in A) was performed with the transfected cells. The lysates were used for anti-CDK9 immunoprecipitation, and the eluates (left panel) or the input (5%) (right panel) were run on SDS gels and immunoblotted with anti-ubiquitin or anti-CDK9 antibodies. The expression of the FLAG-tagged protein was monitored by immunodetection with an anti-FLAG antibody. WB, Western blotting; IP, immunoprecipitation; WCE, whole cell extract.