Abstract
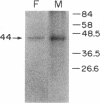
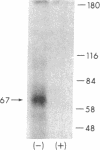
Recent findings from this laboratory suggest that the biological actions of placental lactogen (PL) in mammalian fetal tissues are mediated through binding of the hormone to a distinct and unique PL receptor. We have now purified this receptor from fetal and maternal sheep liver, characterized its binding to PL, growth hormone (GH), and prolactin (PRL), and determined its molecular weight by SDS-PAGE and by affinity cross-linking techniques. Soluble extracts containing specific, high-affinity (Kd 0.5 nM) PL binding activity were prepared by incubating ovine fetal and maternal liver microsomes with 1% Triton X-100. The detergent solubilized PL receptor was purified two- to threefold by ion-exchange chromatography and an additional twofold by gel exclusion chromatography on Sepharose 6B. The PL receptor was then purified 75,000- to 125,000-fold by affinity chromatography using a column of ovine PL (oPL) coupled to Affi-Gel 10. The molecular weight of the oPL receptor as determined by SDS-PAGE and by cross-linking techniques was 44,000 +/- 2,000 (range 40,000-48,000). The purified receptor bound 125I-oPL specifically and with high affinity (Kd 0.5 nM) but did not bind either radiolabeled ovine GH or ovine PRL. In addition, in competition studies using 125I-oPL as the radioligand, the purified PL receptor bound unlabeled oPL with a potency 30-50 times greater than that of ovine GH and 500-1,000 times greater than that of ovine PRL. These findings demonstrate the presence of a specific PL receptor in fetal and maternal sheep liver. The PL receptor, together with the GH and PRL receptors, constitute a family of distinct but related hormone receptors that differ in their relative affinities for PL, GH, and PRL. Changes in the expression of the three receptors may mediate changes in the hormonal control of growth during the transition from fetal to postnatal life.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams S. O., Nissley S. P., Handwerger S., Rechler M. M. Developmental patterns of insulin-like growth factor-I and -II synthesis and regulation in rat fibroblasts. Nature. 1983 Mar 10;302(5904):150–153. doi: 10.1038/302150a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnard R., Waters M. J. Serum and liver cytosolic growth-hormone-binding proteins are antigenically identical with liver membrane 'receptor' types 1 and 2. Biochem J. 1986 Aug 1;237(3):885–892. doi: 10.1042/bj2370885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann G., Stolar M. W., Amburn K., Barsano C. P., DeVries B. C. A specific growth hormone-binding protein in human plasma: initial characterization. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 Jan;62(1):134–141. doi: 10.1210/jcem-62-1-134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boutin J. M., Jolicoeur C., Okamura H., Gagnon J., Edery M., Shirota M., Banville D., Dusanter-Fourt I., Djiane J., Kelly P. A. Cloning and expression of the rat prolactin receptor, a member of the growth hormone/prolactin receptor gene family. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):69–77. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90488-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr D., Friesen H. G. Growth hormone and insulin binding to human liver. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1976 Mar;42(3):484–493. doi: 10.1210/jcem-42-3-484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter-Su C., Schwartz J., Kikuchi G. Identification of a high affinity growth hormone receptor in rat adipocyte membranes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):1099–1104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhanireddy R., Ulane R. E. Prolactin binding in the developing rat fetal liver. Life Sci. 1984 Aug 13;35(7):733–740. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(84)90341-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donner D. B. Covalent coupling of human growth hormone to its receptor on rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2736–2743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freemark M., Comer M., Handwerger S. Placental lactogen and GH receptors in sheep liver: striking differences in ontogeny and function. Am J Physiol. 1986 Sep;251(3 Pt 1):E328–E333. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1986.251.3.E328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freemark M., Comer M., Korner G. Differential solubilization of placental lactogen (PL)- and growth hormone-binding sites: further evidence for a unique PL receptor in fetal and maternal liver. Endocrinology. 1988 Jun;122(6):2771–2779. doi: 10.1210/endo-122-6-2771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freemark M., Comer M., Korner G., Handwerger S. A unique placental lactogen receptor: implications for fetal growth. Endocrinology. 1987 May;120(5):1865–1872. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-5-1865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freemark M., Handwerger S. Ovine placental lactogen inhibits glucagon-induced glycogenolysis in fetal rat hepatocytes. Endocrinology. 1985 Apr;116(4):1275–1280. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-4-1275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freemark M., Handwerger S. Ovine placental lactogen stimulates amino acid transport in rat diaphragm. Endocrinology. 1982 Jun;110(6):2201–2203. doi: 10.1210/endo-110-6-2201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freemark M., Handwerger S. Ovine placental lactogen stimulates glycogen synthesis in fetal rat hepatocytes. Am J Physiol. 1984 Jan;246(1 Pt 1):E21–E24. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1984.246.1.E21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freemark M., Handwerger S. Ovine placental lactogen, but not growth hormone, stimulates amino acid transport in fetal rat diaphragm. Endocrinology. 1983 Jan;112(1):402–404. doi: 10.1210/endo-112-1-402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freemark M., Handwerger S. Synergistic effects of oPL and insulin on glycogen metabolism in fetal rat hepatocytes. Am J Physiol. 1984 Dec;247(6 Pt 1):E714–E718. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1984.247.6.E714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freemark M., Handwerger S. The glycogenic effects of placental lactogen and growth hormone in ovine fetal liver are mediated through binding to specific fetal ovine placental lactogen receptors. Endocrinology. 1986 Feb;118(2):613–618. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-2-613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluckman P. D., Butler J. H., Elliott T. B. The ontogeny of somatotropic binding sites in ovine hepatic membranes. Endocrinology. 1983 May;112(5):1607–1612. doi: 10.1210/endo-112-5-1607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluckman P. D., Grumbach M. M., Kaplan S. L. The neuroendocrine regulation and function of growth hormone and prolactin in the mammalian fetus. Endocr Rev. 1981 Fall;2(4):363–395. doi: 10.1210/edrv-2-4-363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grumbach M. M., Kaplan S. L., Sciarra J. J., Burr I. M. Chorionic growth hormone-prolactin (CGP): secretion, disposition, biologic activity in man, and postulated function as the "growth hormone" of the 2d half of pregnancy. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1968 Feb 5;148(2):501–531. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1968.tb20372.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haeuptle M. T., Aubert M. L., Djiane J., Kraehenbuhl J. P. Binding sites for lactogenic and somatogenic hormones from rabbit mammary gland and liver. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):305–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harigaya T., Smith W. C., Talamantes F. Hepatic placental lactogen receptors during pregnancy in the mouse. Endocrinology. 1988 Apr;122(4):1366–1372. doi: 10.1210/endo-122-4-1366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herington A. C., Ymer S., Stevenson J. Identification and characterization of specific binding proteins for growth hormone in normal human sera. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jun;77(6):1817–1823. doi: 10.1172/JCI112507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. J., Crace C. J., Fowler L., Holder A. T., Milner R. D. Cultured fetal rat myoblasts release peptide growth factors which are immunologically and biologically similar to somatomedin. J Cell Physiol. 1984 Jun;119(3):349–358. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041190314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. J., Crace C. J., Milner R. D. Incorporation of [3H]thymidine by isolated fetal myoblasts and fibroblasts in response to human placental lactogen (HPL): possible mediation of HPL action by release of immunoreactive SM-C. J Cell Physiol. 1985 Nov;125(2):337–344. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041250224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. J., Crace C. J., Strain A. J., Milner R. D. Regulation of amino acid uptake and deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in isolated human fetal fibroblasts and myoblasts: effect of human placental lactogen, somatomedin-C, multiplication-stimulating activity, and insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 Apr;62(4):753–760. doi: 10.1210/jcem-62-4-753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. J., Freemark M., Strain A. J., Handwerger S., Milner R. D. Placental lactogen and growth hormone receptors in human fetal tissues: relationship to fetal plasma human placental lactogen concentrations and fetal growth. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1988 Jun;66(6):1283–1290. doi: 10.1210/jcem-66-6-1283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley T. W., Handwerger S., Fellows R. E. Isolation and structural characterization of ovine placental lactogen. Biochemistry. 1977 Dec 13;16(25):5598–5604. doi: 10.1021/bi00644a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley T. W., Kuhn C. M., Schanberg S. M., Handwerger S. Differential effects of placental lactogen, growth hormone and prolactin on rat liver ornithine decarboxylase activity in the perinatal period. Life Sci. 1980 Dec 8;27(23):2269–2275. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90394-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josimovich J. B., Merisko K., Boccella L., Tobon H. Binding of prolactin by fetal rhesus cell membrane fractions. Endocrinology. 1977 Feb;100(2):557–563. doi: 10.1210/endo-100-2-557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katoh M., Djiane J., Kelly P. A. Prolactin-binding components in rabbit mammary gland: characterization by partial purification and affinity labeling. Endocrinology. 1985 Jun;116(6):2612–2620. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-6-2612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly P. A., Djiane J., Katoh M., Ferland L. H., Houdebine L. M., Teyssot B., Dusanter-Fourt I. The interaction of prolactin with its receptors in target tissues and its mechanism of action. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1984;40:379–439. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571140-1.50014-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly P. A., Posner B. I., Tsushima T., Friesen H. G. Studies of insulin, growth hormone and prolactin binding: ontogenesis, effects of sex and pregnancy. Endocrinology. 1974 Aug;95(2):532–539. doi: 10.1210/endo-95-2-532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesniak M. A., Gorden P., Roth J. Reactivity of non-primate growth hormones and prolactins with human growth hormone receptors on cultured human lymphocytes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1977 May;44(5):838–849. doi: 10.1210/jcem-44-5-838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung D. W., Spencer S. A., Cachianes G., Hammonds R. G., Collins C., Henzel W. J., Barnard R., Waters M. J., Wood W. I. Growth hormone receptor and serum binding protein: purification, cloning and expression. Nature. 1987 Dec 10;330(6148):537–543. doi: 10.1038/330537a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson G. A. Analysis of radioligand binding experiments. A collection of computer programs for the IBM PC. J Pharmacol Methods. 1985 Nov;14(3):213–228. doi: 10.1016/0160-5402(85)90034-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley B. R., Kirsch D. R., Morris N. R. A simplified ultrasensitive silver stain for detecting proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):361–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90470-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Norstedt G., Gelinas R. E., Hammer R. E., Brinster R. L. Metallothionein-human GH fusion genes stimulate growth of mice. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):809–814. doi: 10.1126/science.6356363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkes M. J., Hill D. J. Lack of growth hormone-dependent somatomedins or growth retardation in hypophysectomized fetal lambs. J Endocrinol. 1985 Feb;104(2):193–199. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1040193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilistine S. J., Moses A. C., Munro H. N. Placental lactogen administration reverses the effect of low-protein diet on maternal and fetal serum somatomedin levels in the pregnant rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5853–5857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posner B. I. Characterization and modulation of growth hormone and prolactin binding in mouse liver. Endocrinology. 1976 Mar;98(3):645–654. doi: 10.1210/endo-98-3-645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiu R. P., Kelly P. A., Friesen H. G. Radioreceptor assay for prolactin and other lactogenic hormones. Science. 1973 Jun 1;180(4089):968–971. doi: 10.1126/science.180.4089.968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith W. C., Talamantes F. Identification and characterization of a heterogeneous population of growth hormone receptors in mouse hepatic membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 15;262(5):2213–2219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer S. A., Hammonds R. G., Henzel W. J., Rodriguez H., Waters M. J., Wood W. I. Rabbit liver growth hormone receptor and serum binding protein. Purification, characterization, and sequence. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7862–7867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strain A. J., Hill D. J., Swenne I., Milner R. D. Regulation of DNA synthesis in human fetal hepatocytes by placental lactogen, growth hormone, and insulin-like growth factor I/somatomedin-C. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Jul;132(1):33–40. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041320105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenne I., Hill D. J., Strain A. J., Milner R. D. Effects of human placental lactogen and growth hormone on the production of insulin and somatomedin C/insulin-like growth factor I by human fetal pancreas in tissue culture. J Endocrinol. 1987 May;113(2):297–303. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1130297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsushima T., Friesen H. G. Radioreceptor assay for growth hormone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1973 Aug;37(2):334–337. doi: 10.1210/jcem-37-2-334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]