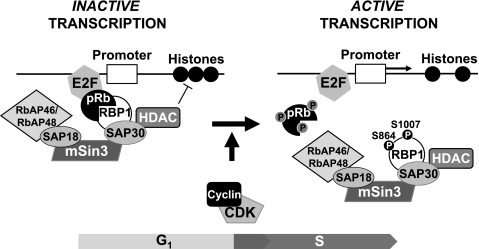
FIGURE 5.
CDK-mediated cumulative phosphorylation of pRb and concurrent phosphorylation of RBP1 promotes their dissociation to mediate release of the SAP30·mSin3·HDAC complex. During G0/G1 phase, when CDK activity is low, the RBP1/pRb interaction mediates HDAC-dependent pRb inhibition on E2F transcription factors. As cells progress into the cell cycle, G1 and S phase CDKs phosphorylate both pRb and RBP1 to disrupt their interaction, removing SAP30·mSin3·HDACs from pRb and E2F and thereby allowing transcription of genes necessary for S phase cell cycle progression.