Figure 1.
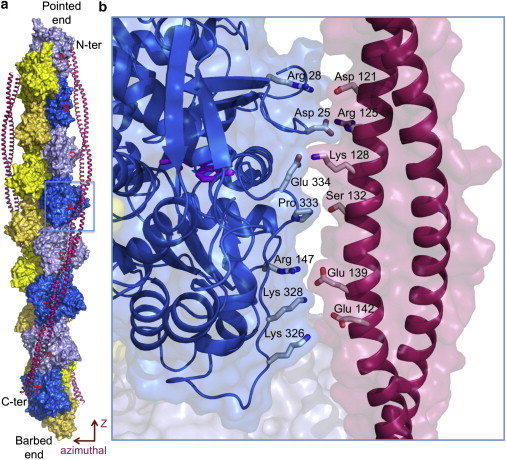
Model of tropomyosin on the actin filament as proposed by Li et al. (1). (a) Tropomyosin winds symmetrically along the two long-pitch helices of the actin filament, making similar contacts with each actin subunit (numbered) along its 385-Å-long path. (b) Close-up view of tropomyosin pseudo-repeat-4 (contoured in panel a, but slightly rotated), which together with pseudo-repeat-5 makes the strongest contacts with the filament (4). Positively charged amino acids of actin subdomain 4 (Arg-147, Lys-326, and Lys-328) face negatively charged amino acids in each pseudo-repeat of tropomyosin. Pro-333 in a protruding loop of actin, running from subdomain 3 to 1, faces a shallow area of tropomyosin. Additional contacts may involve Glu-334, Arg-28, and Asp-25 in actin subdomain 1, which face oppositely charged amino acids in tropomyosin. Similar contacts are observed along all seven pseudo-repeats of tropomyosin.
