Figure 4.
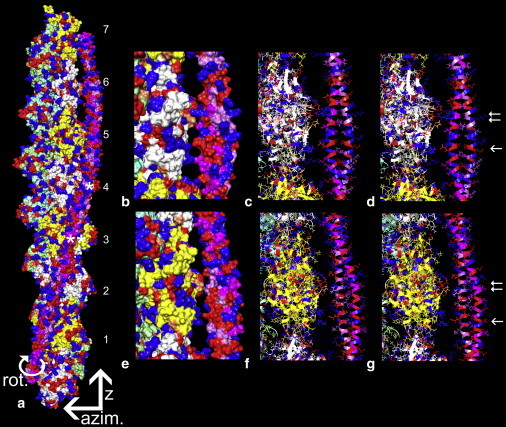
Optimal electrostatic interactions between F-actin and tropomyosin. (a) Surface view showing the location of tropomyosin on F-actin that optimizes electrostatic interactions between the two structures. The rotation, azimuthal, and z directions discussed in the text are indicated by arrows. The pointed end of F-actin is facing up (as the arrow for z indicates) and actin subunits are numbered as in Table 1, tropomyosin quasi-repeat 4 is marked with a single asterisk and quasi-repeat 5 with a double asterisk (note that, by convention, the numbering of actin subunits and tropomyosin repeats do not match). (b and e) Segments of the F-actin-tropomyosin model in panel a are enlarged and rotated to highlight potential interactions of tropomyosin quasi-repeats 4 (b) and quasi-repeat 5 (e) with actin subunits. (c and f) The same as b and e but in wire/ribbon format. (d and g) The corresponding region of F-actin as in c and f, but here displaying the alignment of F-actin and tropomyosin models that were fitted into the F-actin-tropomyosin reconstruction (note that the relative positions of interacting amino acids correspond closely to those in c and f). The single arrow in g points to Lys-326, Arg-147, and Lys-328 residues of actin subunit 3 approaching Glu-181 on tropomyosin quasi-repeat 5, and the single arrow in d points to Arg-147 and Lys-328 of actin subunit 4 approaching residue Glu-139 on tropomyosin repeat 4. The double arrows point to actin Pro-333 on actin subunits 3 and 4 approaching Val-170 and Ser-132 on tropomyosin repeats 5 and 4, as well as to actin Asp-25 and Arg-28 close to Arg-167 and Glu-163 on tropomyosin repeat 5, and Lys-128, Arg-125, and Asp-121 on repeat 4. Each of the other tropomyosin quasi-repeats shows a similar but not identical pattern of interactions with respective actin subunits (not displayed; see Table 1). Basic amino acid residues in actin and tropomyosin are painted blue, acidic amino acids are red, and proline is coral. An identical grid search was performed to determine the optimal electrostatic interaction for tropomyosin with the recently published F-actin structure proposed by the Namba Laboratory (41). The z-position determined for tropomyosin on this model was the same as that found for the Oda model (22).
