Figure 5.
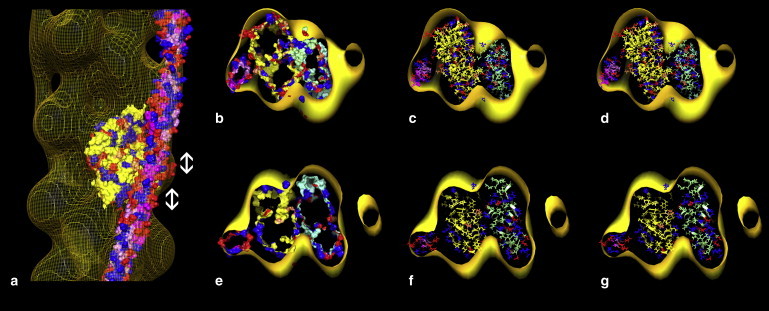
Relative location of tropomyosin and actin in the EM reconstruction of F-actin-tropomyosin. (a) Surface view of the reconstruction shown in yellow wire mesh to facilitate inspection of docked proteins. Here, both tropomyosin and F-actin models were fitted separately into the reconstruction using Chimera fitting tools (the atomic structure of just one of the docked actin subunits is displayed). (b–g) Cross-sections of actin viewed from the barbed end of F-actin (here, a was rotated by ∼180° before sectioning). Two cross-sections through regions of actin subunit 3 and tropomyosin repeat 5 are indicated by double-ended arrows in panel a and shown in b, c, e, and f. The outer boundaries of the docked actin and tropomyosin are shown as isosurfaces in b and e, and in more detail in wire/ribbon format in c and f. (b and c) Val-170, Arg-167, and Glu-163 on tropomyosin are seen oriented toward Pro-333, Asp-25, and Arg-28 on actin. (e and f) Glu-181 on tropomyosin is oriented toward Lys-326, Lys-328, and Arg-147 on actin. Note the perpendicular orientation of the tropomyosin elliptical axis with respect to the charged surface of actin. (This same arrangement is also seen over corresponding sections of the other tropomyosin quasi-repeats.) (d and g) The identical region of maps as in c and f, but here displaying the optimal alignment of F-actin and tropomyosin based on electrostatics, as in Fig. 4. Color-coding of amino acids is the same as in Fig. 4.
