Figure 4.
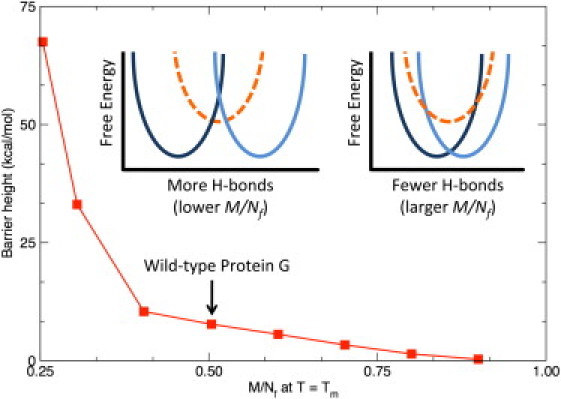
Using Protein G as an example, the straddling barrier height is plotted versus at the respective Tm for each. (Insets) Adding H-bonds (smaller values of ) separates the basins, thus increasing the barrier height. In addition to the native and unfolded basins, additional states (dashed) are possible, but their probabilities are generally zero; yet they do emerge when the barrier height is increased as . Conversely, the barrier height is suppressed as because the basins share greater overlap, transforming into a continuous transition, and then eventually no transition without any H-bonds. (Highlighted) The wild-type value () for Protein G.
