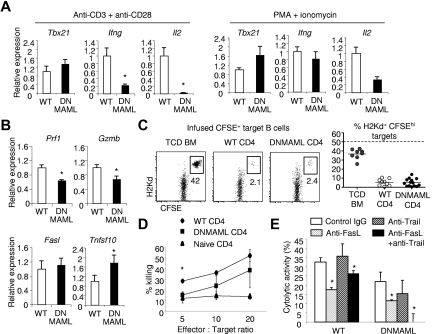
Figure 5.
Hyporesponsiveness of alloreactive DNMAML CD4+ T cells to CD3/CD28-mediated signals, but significant preservation of cytotoxic potential. CFSElow donor-derived WT or DNMAML CD4+ T cells were sort-purified at day 5 after transplantation into lethally irradiated (900 rads) BALB/c hosts. The cells were restimulated ex vivo during 6 hours with plate-bound anti-CD3/anti-CD28, or with PMA and ionomycin. (A) Decreased Il2 transcripts and impaired expression of Ifng despite normal induction of Tbx21 (encoding T-bet) in DNMAML CD4+ T cells after stimulation with anti-CD3/anti-CD28 antibodies. PMA and ionomycin could partially rescue Il2 and fully induce Ifng expression. (B) Modest decrease in Prf1 and Gzmb transcripts, but preserved induction of Fasl and Tnfsf10 mRNA (encoding Trail) in DNMAML CD4+ T cells. (C) In vivo cytotoxic activity of WT or DNMAML CD4+ T cells against infused CFSEhi host-type BALB/c (H-2d) B cell targets, compared with control CFSElo B6-SJL cells (H-2b). Analysis was performed on day 14, 18 hours after infusion of CFSE-labeled targets at a 1:1 ratio (107 each). Data are shown as percent residual CFSEhiH-2Kd+ cells among all infused CFSE-labeled B cells. The dotted line represents expected recovery in the absence of cytotoxicity. (D) In vitro cytotoxic activity of WT or DNMAML CD4+ T cells against A20 leukemia cells. *P < .05 (2-tailed unpaired Student t test). (E) Inhibition of in vitro cytotoxic activity of DNMAML CD4+ T cells by anti-FasL and anti-Trail antibodies. *P < .05 (2-tailed unpaired Student t test).