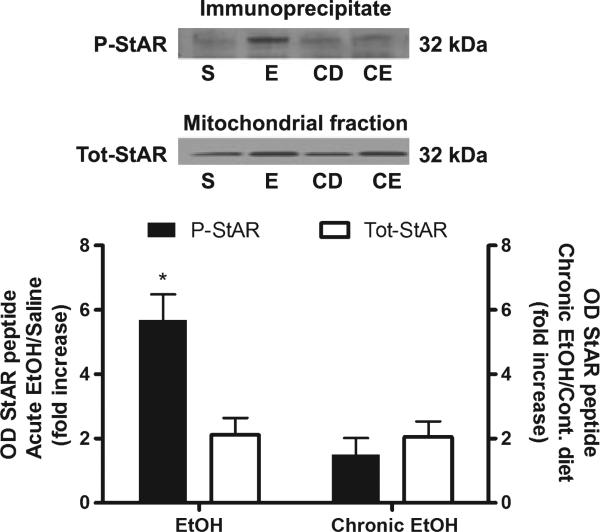
Fig. 4.
Chronic ethanol exposure results in tolerance to increased phosphorylation of adrenal StAR protein. Adrenal fractions were immunoprecipitated with phospho-PKA substrate antibody, separated by SDS–PAGE and probed with StAR. A representative blot is shown above the bar graph. For acute ethanol (E), results are reported as fold increase of phospho-StAR (P-StAR) compared to saline (S). For chronic ethanol (CE) exposure, results are reported as fold increase of phospho-StAR compared to control diet (CD). The fold increase of total StAR (Tot-StAR) protein for both acute and chronic ethanol was also measured and compared to its respective control. *p < 0.01 compared to total star for acute ethanol (Student's t-test), n =4.