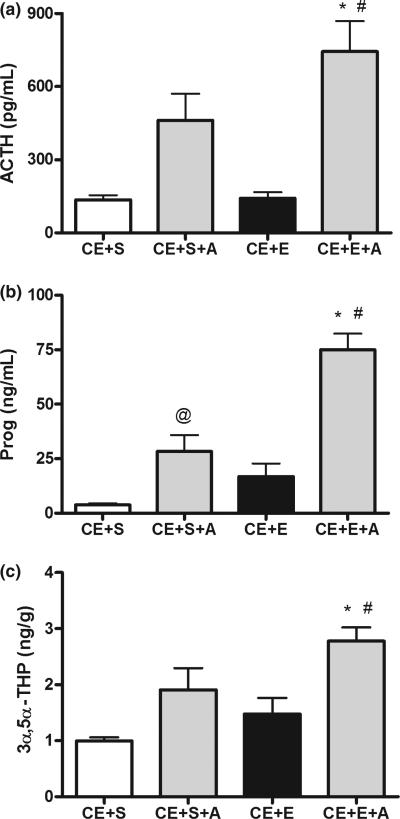
Fig. 5.
Exogenous ACTH replacement restores serum and brain neuroactive steroid levels following chronic ethanol exposure. Rats exposed to chronic dietary ethanol were challenged with saline or ethanol (CE + S and CE + E, respectively). ACTH (2 μg, i.p.) was administered along with the saline or ethanol challenge (CE + S + A and CE + E + A, respectively). Tissues were collected 60 min after challenge and serum (a) ACTH and (b) progesterone, as well as (c) cerebral cortical 3α,5α-THP were measured. *p < 0.001 compared to CE + S, #p < 0.05 compared to CE + S + A and CE + E, and @p < 0.05 compared to CE + S (anova followed by Newman–Keuls test), n = 8–9 in duplicate.