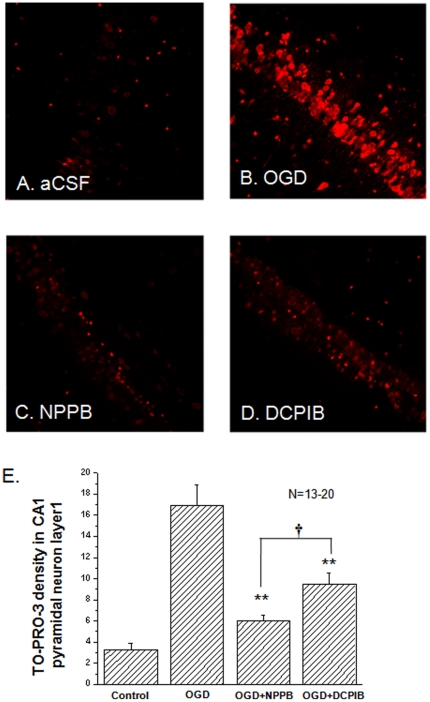
Figure 6. The effects of NPPB and DCPIB on OGD induced pyramidal neuron death.
Besides the control group (in aCSF, A), the hippocampal slices were randomly divided into three groups after 25 min OGD treatment to receive the following post-OGD treatment: 1) in bath solution (B. OGD); 2) bath solution+100 µM NPPB (C. NPPB); and 3) bath solution+10 µM DCPIB (D. DCPIB). The fluorescence density of the TO-PRO-3-I staining is proportional to the neuronal death. Between the aCSF control and the OGD group, the neuronal death increased by 5.3 fold (3.2±0.6 in aCSF vs. 16.9±1.9 in OGD, n = 13). The neuronal death was reduced to 6.0 ±0.5 (n = 20) by 100 µM NPPB, and to 9.4±1.1 (n = 20) by 10 µM DCPIB. Both NPPB and DCPIB were added in the reperfusion bath solution to inhibit post-OGD VRAC. All the fluorescence intensity values are arbitrary. **. The difference between the OGD and NPPB or DCPIB groups is statistically significant at p≤0.01t. †. The difference between the NPPB and DCPIB groups is statistically significant at p≤0.05.