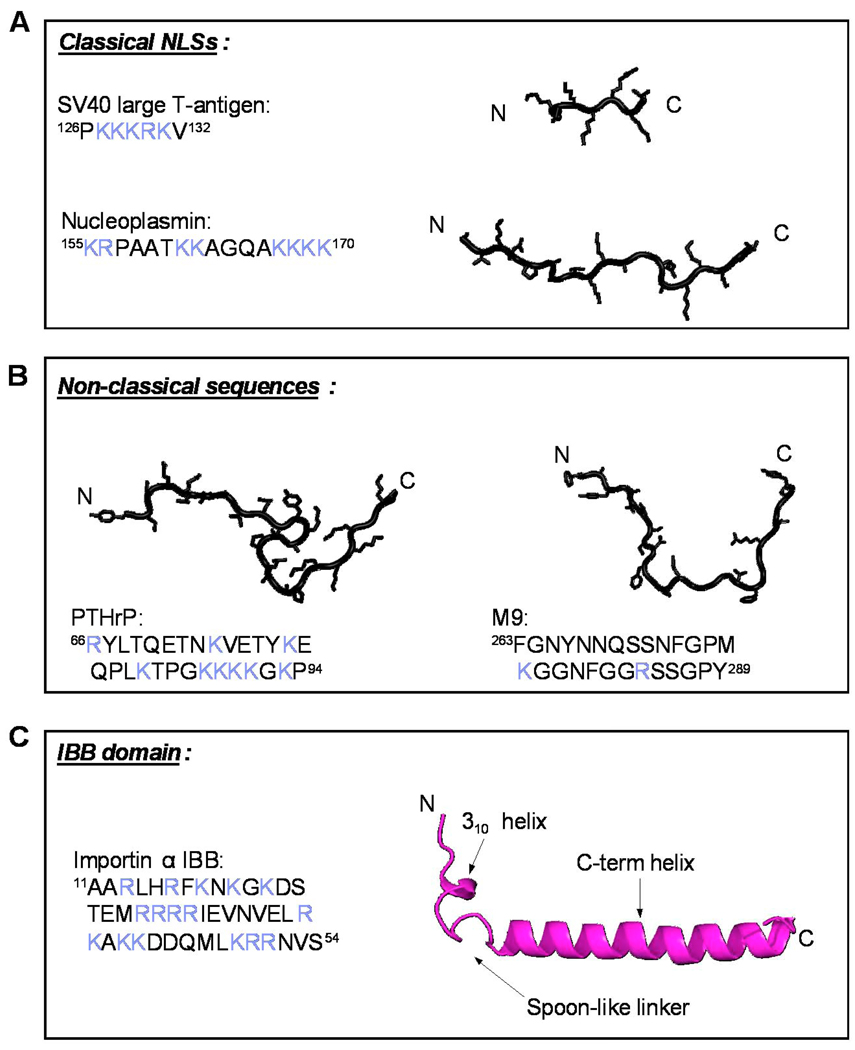
Fig. 1. Diversification of NLSs three-dimensional structure and amino acid sequence.
All structures are taken from the crystallographic complexes of the NLS bound to their respective receptor/adaptor. In the amino acid sequence, basic amino acids are colored in blue. (A) Classical monopartite and bipartite NLS found in SV40 T-large antigen (pdb 1EJL) and nucleoplasmin (pdb 1EJY) (top and bottom, respectively) that bind importin α. (B) Extended non-classical NLSs recognized directly by β-karyopherins. In the left panel is the PTHrP-NLS (res. 67–94) (pdb 1M5N) that binds importin β N-terminal HEAT repeats 1–11 [13]. In the right panel is the M9-NLS of hnRNP A1, which binds transportin (pdb 2H4M) [12]. (C) Ribbon diagram of importin α IBB-domain (pdb 1QGK). This ∼40 amino acid domain contains an N-terminal 310 helix connected by a loop of variable length to a long C-terminal α-helix.