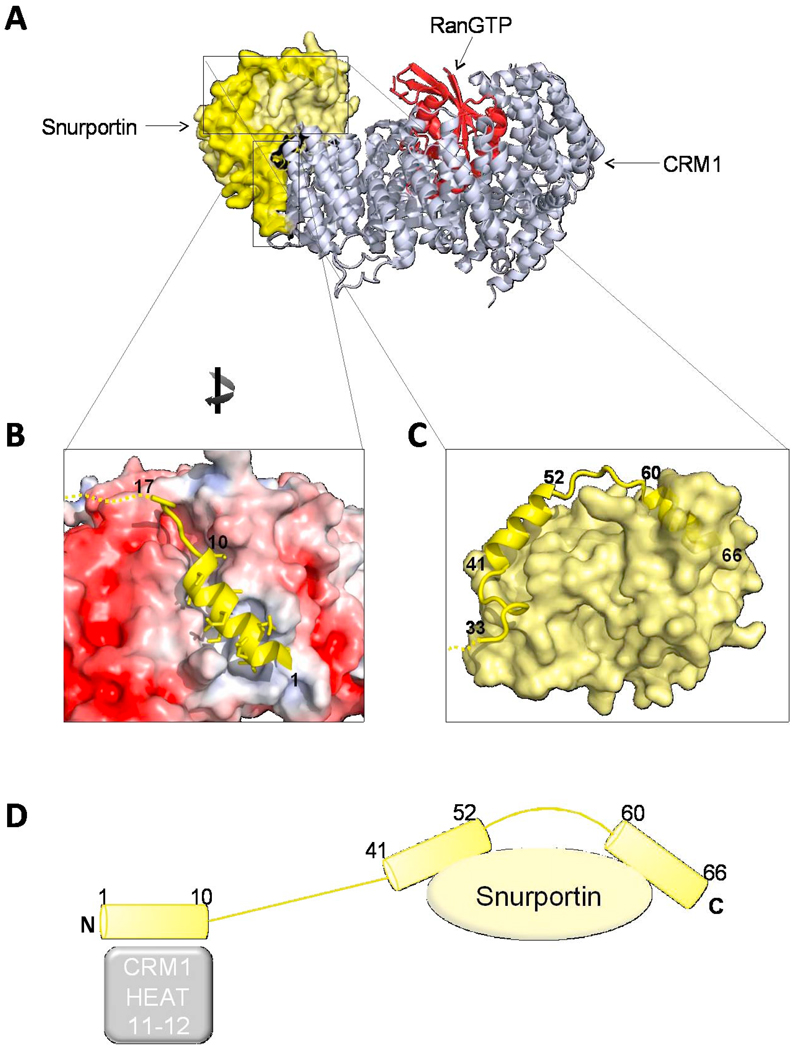
Fig. 8. Structure of the sIBB in the snurportin/CRM1/RanGTP export complex.
(A) Structure of the snurportin export complex formed by CRM1 (silver ribbon), RanGTP (red ribbon) and snurportin (shown as a light yellow surface) (pdb 3GJX) [104], with the sIBB highlighted as a yellow cartoon. (B) The N-terminus of the sIBB (shown as a yellow helix) occupies a hydrophobic cleft formed by CRM1 HEAT repeats 11–12. In the diagram, the acidic surface of CRM1 electrostatic potential map is colored in red, while the NES binding groove, which is more hydrophobic, is in white. (C) Magnification of sIBB residues 41–66 bound as an interrupted helix to the main body of snurportin. The sIBB is shown as a yellow ribbon, while snurportin main body is shown as a yellow surface. The surface exposed kink between sIBB helix 41–52 and 60–66 is a possible target for importin β. (D) Schematic representation of the sIBB-domain emphasizing its extended interactions with CRM1 (silver) and snurportin (yellow).