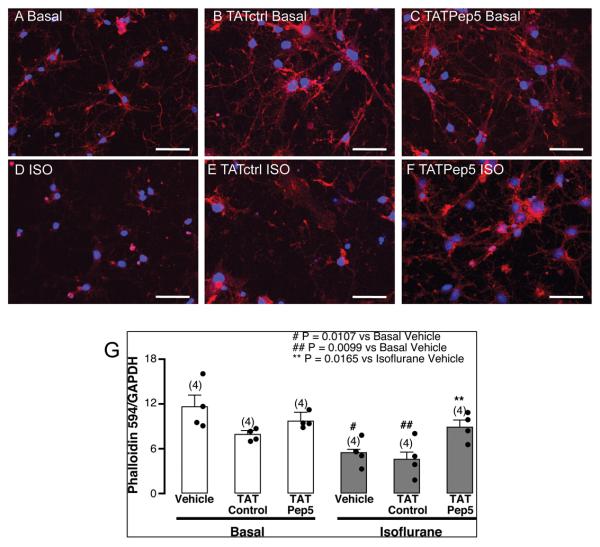
Fig. 5.
TAT-Pep5 decreases isoflurane-mediated reduction in phalloidin immunofluorescence. Primary neurons (4-7 days in vitro – DIV4-7) were exposed to 1.4% isoflurane for 3 h with or without pretreatment with TATctrl (10 μM, 15 min) and TAT-Pep5 (10 μM, 15 min) and stained with the actin binding toxin phalloidin (conjugated to Alexa-594) and the nuclear marker DAPI. Phalloidin (red pixels) is normalized to DAPI (blue pixels). A) basal, B) TATctrl basal, C) TAT-Pep5 basal, D) isoflurane, E) TATctrl isoflurane, F) TAT-Pep5 isoflurane. Exposure of DIV4-7 neurons to isoflurane significantly (n = 4; # p = 0.0107 vs. basal, p = 0.0094 vs. TATctrl basal, p = 0.0237 vs. TAT-Pep5 basal) decreased phalloidin immunofluorescence (D). Isoflurane-mediated effects were significantly attenuated by TAT-Pep5 (** p = 0.0165 vs. isoflurane, p = 0.019 vs. TATctrl isoflurane). Pretreatment with TATctrl did not attenuate the neurotoxic effects from isoflurane (## p = 0.0099 vs. basal, p = 0.0209 vs. TATctrl basal, p = 0.0213 vs. TAT-Pep5 basal). Scale bar, 50 μm. Quantitation of the data is represented in panel G. Error bars, standard error of the mean (s.e.m.).