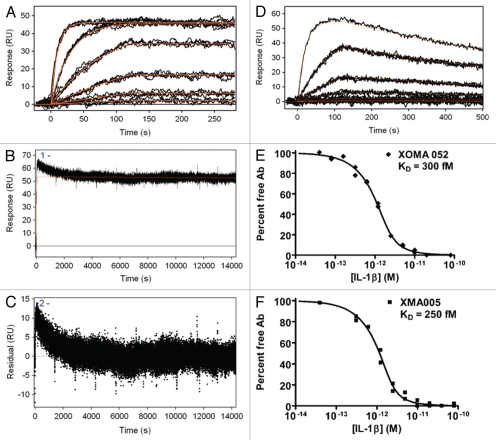
Figure 1.
Kinetic binding analysis of XOMA 052 and XMA005. (A) Injection of human IL-1β over XOMA 052 captured by protein A/G. Data were collected in triplicate for six IL-1β concentrations ranging from 23 pM to 57.8 nM. (B) Three injections of 57.8 nM human IL-1β were followed for 4 h of dissociation and fit using Scrubber2 software to estimate a dissociation rate (kd) of ≤6.3 × 10−6 sec−1. (C) The trend in the residuals from the fit of the data in the early part of dissociation profile is not seen in experiments using aldehyde-coupled antibody and is thus believed to result from instability due to capture. The value for the dissociation rate was determined from the later portion of the long dissociations. The association rate of 1.7 × 106 M−1s−1 was determined using a global fit of the association curves with a simple 1:1 Langmuir binding model with the dissociation rate fixed at the value determined from the long dissociations. The fit of the data is shown as a solid red line, yielding an affinity of ≤4 pM. (D) Injection of mouse IL-1β over XOMA 052 captured by protein A/G. Data were collected in triplicate for six IL-1β concentrations ranging from 23 pM to 300 nM, except for the highest concentration, which was a singlicate injection. Data were fit globally with a simple 1:1 Langmuir binding model, yielding an affinity of 7 nM. Analysis of XOMA 052 (E) and XMA005 (F) binding to human IL-1β by Kinetic Exclusion Assay (KinExA). This solution-based method yields equilibrium binding constants (KD) of 300 and 240 fM with 95% confidence intervals of 115 to 742 and 70 to 722 fM, for XOMA 052 and XMA005, respectively.