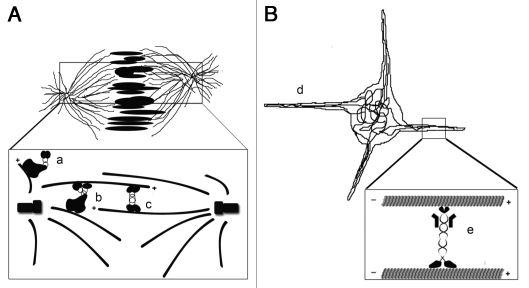
Figure 1.
Molecular motors organize microtubules to facilitate microtubule-mediated force production. (A) The mitotic spindle is organized by three motor proteins and drives the separation of chromosomes into daughter cells. The motors include the dynein/dynactin complex, which functions to anchor the centrosomes to the cell cortex (a), and anchor microtubule minus ends to the centrosome (b). The kinesin 5 motor (c) pushes the two centrosomes apart by crosslinking and sliding anti-parallel microtubules. (B) Our recent study shows that the growth of cellular processes filled with microtubule bundles (d) is powered by microtubule sliding by kinesin-1 heavy chain (e) in interphase cells.23