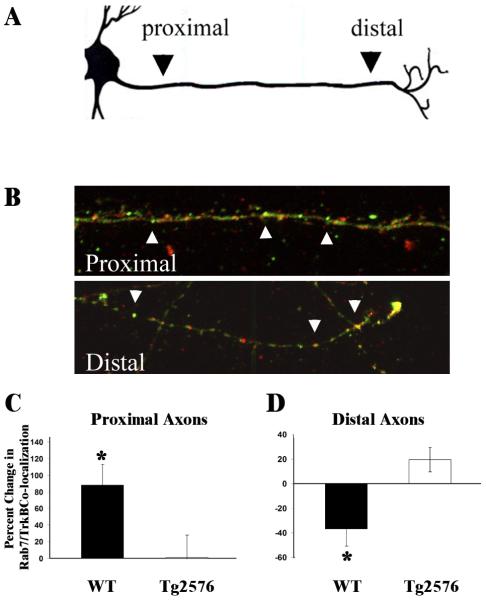
Figure 2.
Retrograde transport of TrkB/Rab7-positive endosomes is impaired in Tg2576 neurons. (A) The co-localization between TrkB and Rab7 was determined in proximal and distal axons at both 10 and 60 min. (B) In axons from mouse primary neurons, co-localization (yellow) between Rab7 (green) and TrkB (red) can be found within puncta in both proximal and distal regions. Representative images from both axonal regions are depicted. The percent change in Rab7/TrkB co-localization between 60 min and 10 min in proximal (C) and in distal (D) axons was determined and was used as an indirect measure of BDNF transport. The data are presented as mean± SEM. The percent change in the co-localization within both proximal and distal axons of WT neurons was significant (*)(p<0.05, n=4 and n=5, respectively). In the case of Tg2576 neurons, the percent increase of co-localization in proximal axons was reduced when compared to WT (88.0% increase vs. 1.3%) and was not significant (**). As TrkB undergoes retrograde transport, an expected decrease in TrkB/Rab7 co-localization is observed in the distal axons of WT neurons (−36.7%), while we observed an increase in the distal axons of Tg2576 (19.6%), but was also not significant.