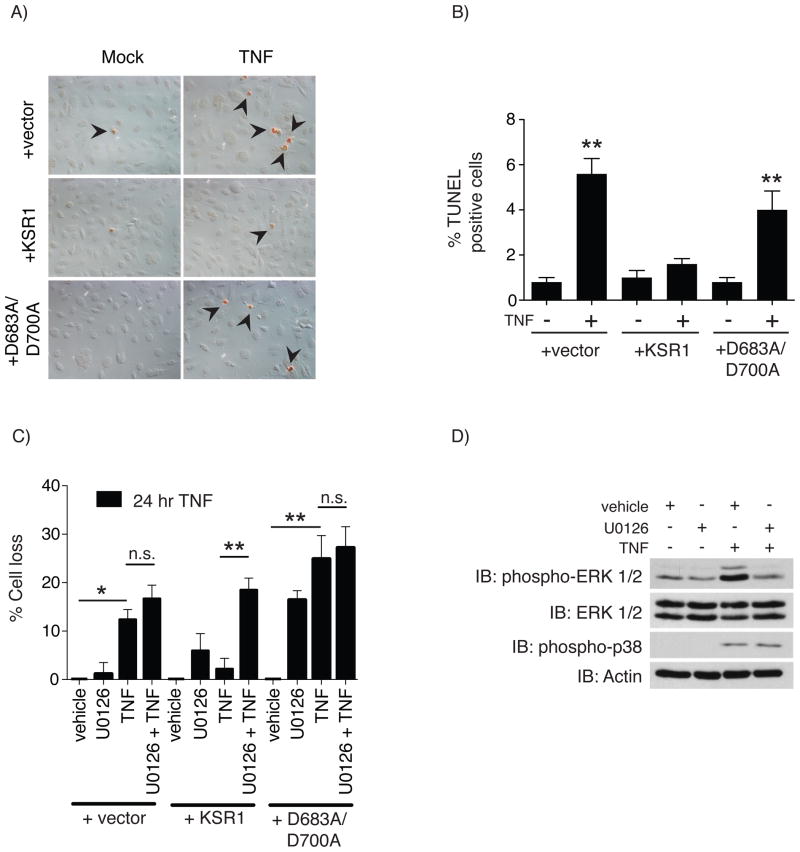
Fig. 2.
KSR1-mediated protection against TNF-induced apoptosis requires both a functional KSR1 kinase domain and MEK kinase activity. A) TNF-induced apoptosis was determined by treating serum-starved +vector, +KSR1, and +D683A/D700A cells with TNF (100 ng/ml) for 8 hours. Apoptotic nuclei were labeled using terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL). B) Apoptotic cells from panel A were quantified and reported as the percentage of TUNEL positive cells out of 500 cells. Solid bars represent the mean for each condition and the error bars the SEM. C) TNF-induced cell loss was determined for cells that were pre-treated with vehicle or the MEK inhibitor U0126 (10 μM) for 45 minutes followed by TNF (100 ng/ml) for 24 hours. The total number of adherent cells was quantified and cell loss calculated as the percent of the vehicle treated control for each cell line. Assays were performed a minimum of 3 times. D) The specificity of U0126 was confirmed in +KSR1 cells pretreated with vehicle or U0126 (10 μM) for 45 minutes followed by TNF for 15 minutes and assayed for phosphorylated ERK. Protein phosphorylation and total protein were determined by Western blot analysis using the indicated antibodies. Immunoblots are representatives of at least 3 independent experiments. * = P < 0.05, ** = P < 0.01, *** = P < 0.001