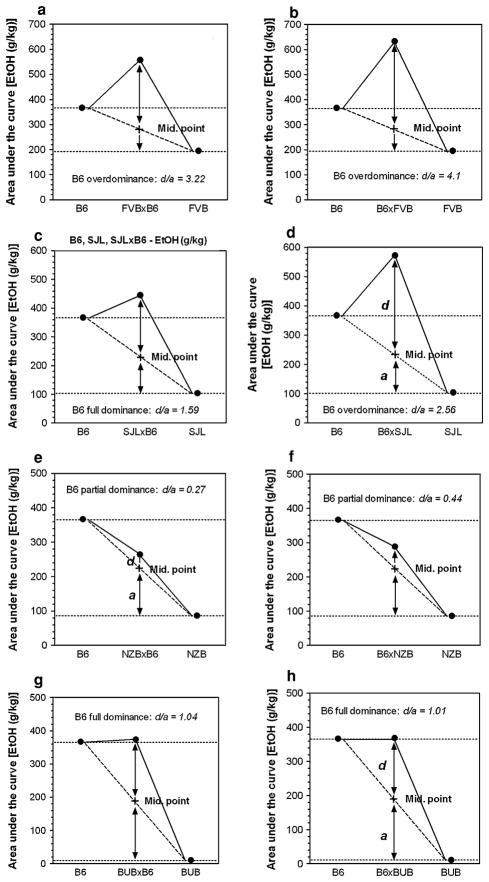
Fig. 9.
Examples of partial dominance, full dominance and overdominance of the B6 allele relative to the NZB, BUB, SJL and FVB. a Phenotypic means for B6, FVB and FVBxB6 F1 hybrids. b Phenotypic means for B6, FVB and B6xFVB F1 hybrids. c Phenotypic means for B6, SJL and SJLxB6 F1 hybrids. d Phenotypic means for B6, SJL and B6xSJL F1 hybrids. e Phenotypic means for B6, NZB and NZBxB6 F1 hybrids. f Phenotypic means for B6, NZB and B6xNZB F1 hybrids. g Phenotypic means for B6, BUB and BUBxB6 F1 hybrids. h Phenotypic means for B6, BUB and B6xBUB F1 hybrids. The area under the curve for ethanol intake (g/kg/24 h) vs. concentrations of ethanol solution for each genotype was used as the phenotypic mean. These areas were calculated from data shown in Figs. 1 and 2