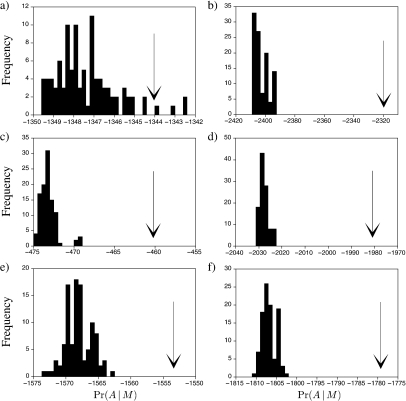
FIGURE 2.
Comparison of the marginal likelihood for the traditional method for assigning branch-length parameters to a tree (arrow) versus random permutations of the traditional method, each of which does not take into account the varying opportunities for substitution along long and short branches of the tree. The graphs depict the results for the sequence alignments of a) gophers, b) fish of the family Labridae, c) seed plants of the family Ericales, d) primates, e) vertebrate ATPase8 gene, and f) vertebrate ND4L gene.