Figure 6.
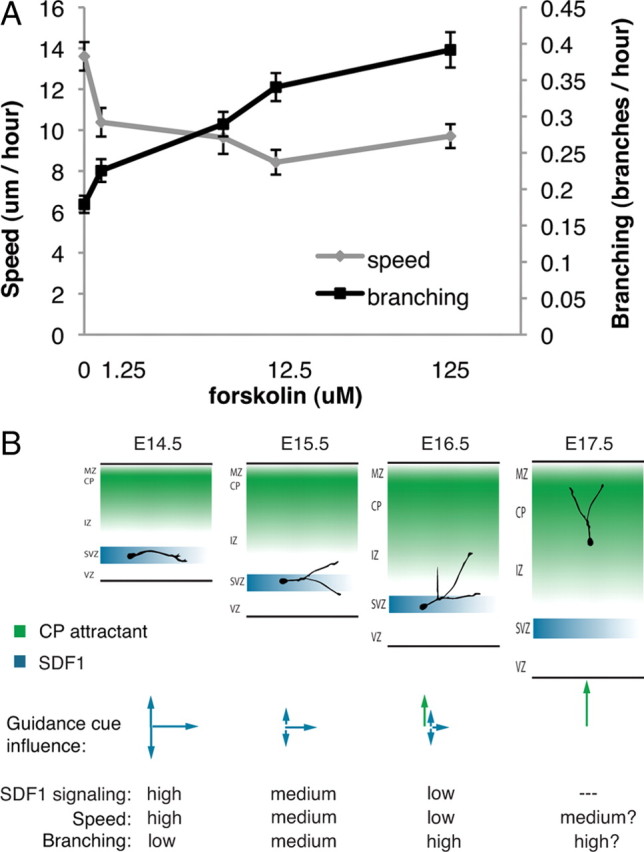
Speed and branching frequency are inversely related. A, Interneurons show a dose-dependent increase in branching frequency when treated with forskolin. As the branching frequency increases, the average speed of migration decreases. Doses in μm: 0, 1.25, 6.25, 12.5, 125. Error bars are ± SEM; 75 cells for each dose; three independent experiments. B, Proposed model for leading process branching initiation of interneuron exit from migration streams. E14.5, An interneuron migrating in the SDF1-rich SVZ/IZ stream branches infrequently and migrates fast. E15.5, As developmental time goes on, SDF1 signaling decreases, increasing branching frequency and slowing the interneuron. E16.5, Increased branching exposes the interneuron to additional guidance factors, inducing a change in migration behavior and stream exit. E17.5, The interneuron is fully under cortical plate (CP) attractant control and reaches its destination in the cortical plate.
