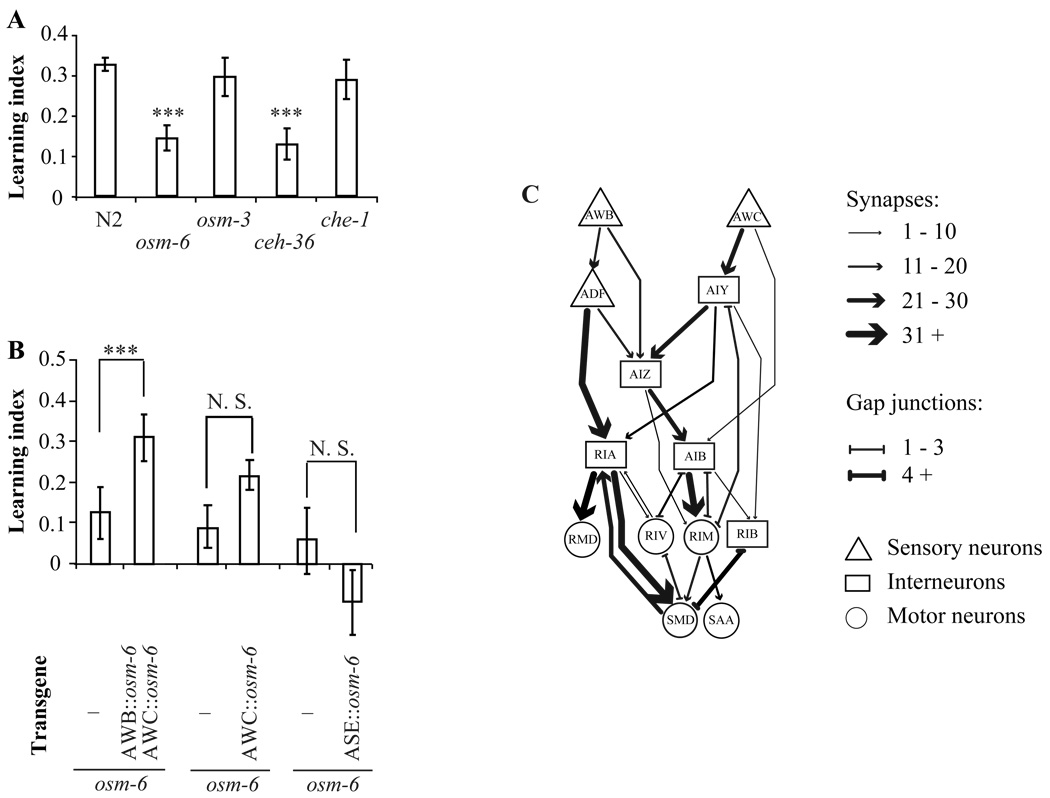
Figure 2. Aversive olfactory learning requires the AWB and AWC olfactory sensory neurons.
A, The aversive olfactory learning ability of wild type animals and chemosensory mutants. The learning ability of mutants and wild type animals were compared with two tailed Student’s t-test and multiple comparisons were adjusted with Bonferroni correction (Data are presented as mean +/− SEM. *** P < 0.001, n ≥ 6 assays, error bars: SEM). B, Expression of osm-6 cDNA in AWB and AWC olfactory sensory neurons rescues the learning defect of osm-6 mutants, but the expression of osm-6 cDNA in the AWC or in the gustatory neurons ASE does not rescue. The learning ability of transgenic animals was compared with that of non-transgenic siblings with paired two tailed Student’s t-test (Data are presented as mean +/− SEM. *** P < 0.001, n ≥ 4 assays, error bars: SEM, N.S.: not significant). C, A candidate neuronal network downstream of sensory neurons AWB and AWC to regulate aversive olfactory learning. Please also see Supplemental Figure 2 and Supplemental Table 1 and 2.