Figure 4. Nutrient deprivation drives assembly of Exo84/Beclin1 complexes.
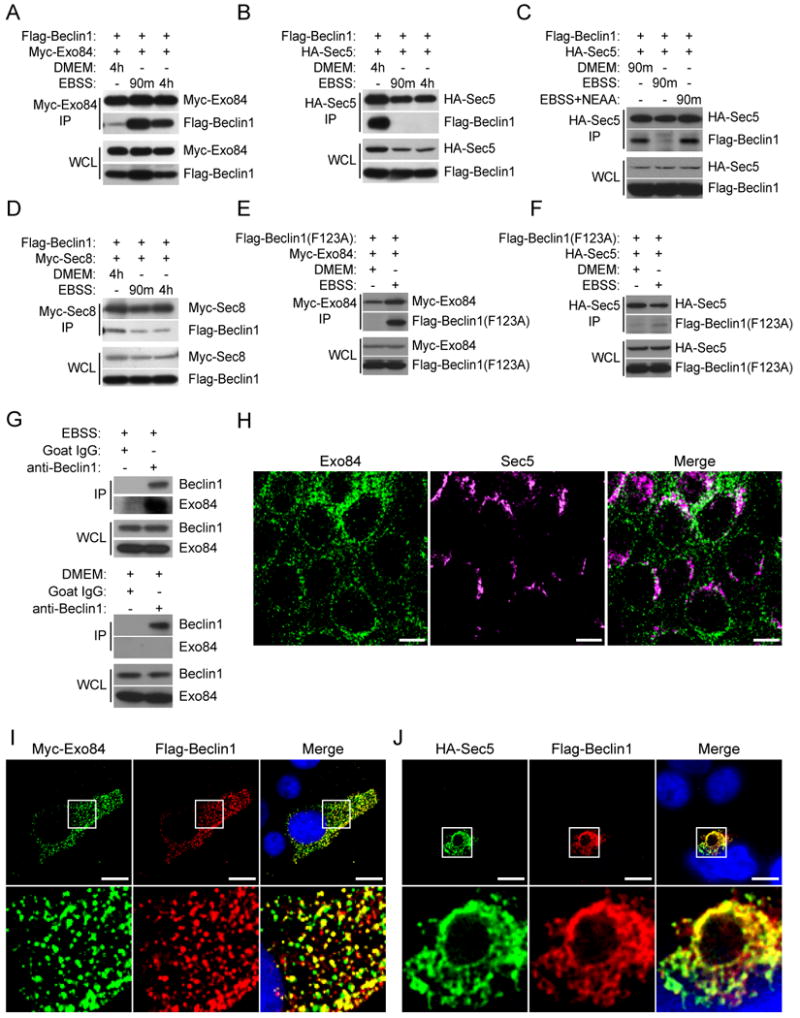
A-D: Nutrient limitation induces Beclin1/Exo84 interactions and inhibits Beclin1/Sec5 interactions. 48 hours post-transfection with tagged Beclin1 and exocyst expression constructs, HEK-293 cells were incubated in DMEM, EBSS, or EBSS with 1× Non-Essential amino acids for 90 minutes or 4 hours as shown. The indicated proteins were then immunoprecipitated with antibodies directed to the specified tag. Immunoprecipitates were analyzed for coprecipitation with Flag-Beclin1. Whole cell lysate (WCL), Immunoprecipitates (IP).
E,F: Beclin1(F123A) mutant interacts with Exo84 but not Sec5. Co-expression, co-IPs with the indicated proteins were performed as in (A-D).
G: Endogenous Beclin1/Exo84 complexes accumulate in response to nutrient deprivation. Endogenous Beclin1 was immunoprecipitated from HEK-293 cells incubated in EBSS (top panels) or DMEM (bottom panels) for 90 minutes and analyzed for coprecipitation of Exo84 (IP). Host species-matched non-specific IgG immunoprecipitates served as negative controls. Representation of the examined proteins in the input whole cell non-denaturing lysates is shown (WCL).
H: Exo84 and Sec5 are enriched in distinct subcellular compartments. Endogenous immunofluorescence of Sec5 (anti-Sec5) and Exo84 (anti-Exo84) in MDCK cells. Scale bar 10μm.
I,J: Exo84 and Sec5 can recruit Beclin1 to distinct subcellular compartments. HEK-293 cells were transfected with (F) Flag-Beclin1 and Myc-Exo84; (G) Flag-Beclin1 and HA-Sec5. Immunofluorescence of the indicated fusion tags was performed. High magnification of 10μm × 10μm regions indicated by the boxes are shown in the bottom panels. Scale bar 10μm.
See also Figure S2.
