Figure 7. Active ULK1 associates with Exo84.
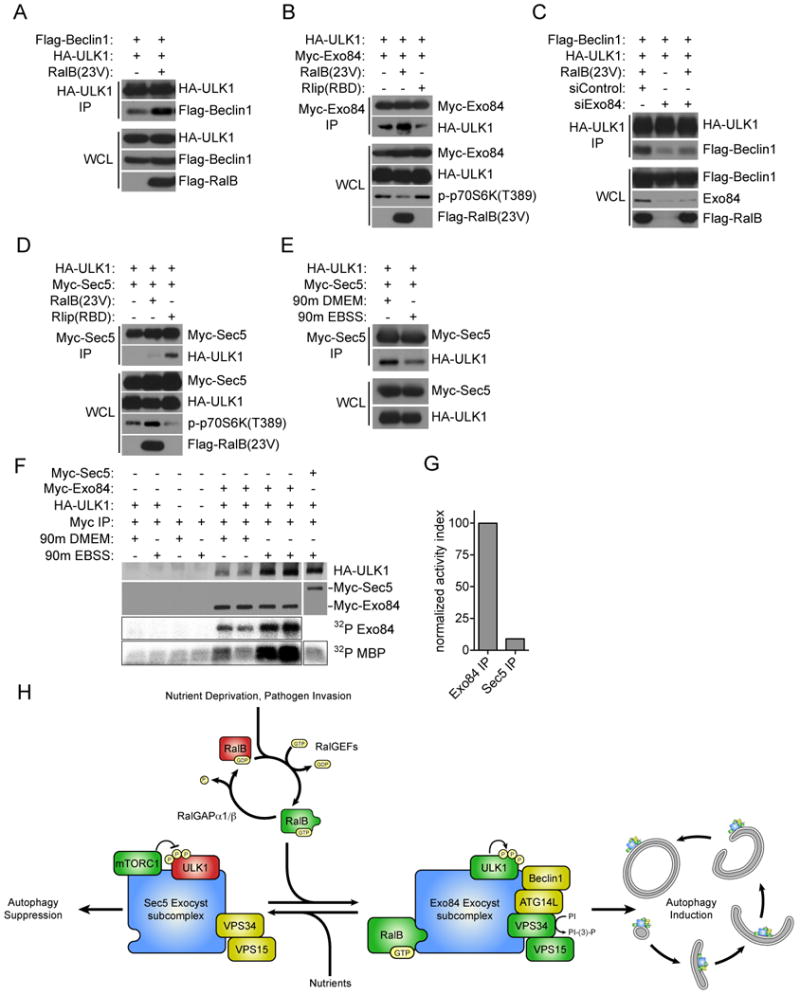
A: RalB induces ULK1/Beclin1 Complex formation. ULK1 immunoprecipitates were analyzed for coprecipitation with Flag-Beclin1 upon RalB(23V) expression as indicated.
B: ULK1/Exo84 complexes are regulated by RalB. The indicated proteins were expressed in HEK-293 cells. Myc-tagged Exo84 was immunoprecipitated and analyzed for coprecipitation with HA-ULK1.
C: RalB induced ULK1/Beclin1 complexes require Exo84. HEK-293 cells were first transfected with siControl or siExo84 siRNAs before the indicated proteins were expressed 24 hours later. ULK1 immunoprecipitates were analyzed for coprecipitation with Flag-Beclin1 upon RalB(23V) expression as indicated.
D: ULK1/Sec5 complexes accumulate upon Ral inhibition. Co-expression, co-IPs with the indicated proteins were performed as in (B).
E: ULK1/Sec5 complexes dissociate upon nutrient deprivation. Co-expression, co-IPs with the indicated proteins were performed as in (B) with the addition of 90 minute incubation in DMEM or EBSS as indicated.
F: Amino-acid starvation induces association of Exo84 with catalytically active ULK1. Exo84 and Sec5 complexes were assayed for coprecipitation with ULK1 and for associated protein kinase activity as indicated.
G: The normalized activity ratio for EBSS stimulated Exo84 and Sec5 precipitates was calculated by the division of MBP 32P incorporation by the HA-ULK1 signal coprecipitated from (F).
H: Working model of RalB/exocyst dependent mobilization of autophagy.
See also Figure S3.
