Figure 6.
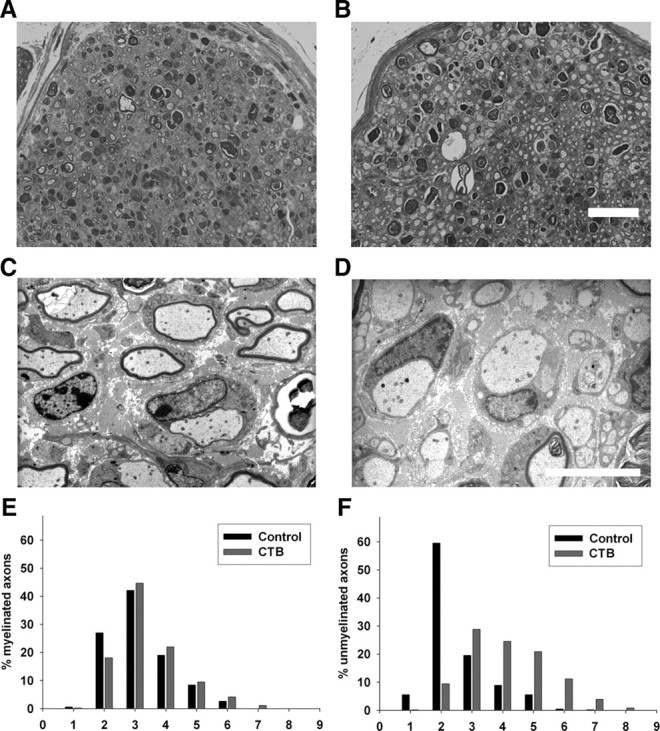
Cholera toxin B-mediated inhibition of peripheral nerve repair. A–D, Light (A, B) and electron (C, D) micrographs of sciatic nerve S2 segments. A, B, Many regenerating fibers are present in both vehicle (A)- and CTB (B)-treated nerves. Scale bar, 2 μm. C, D, Normally myelinating fibers are present in the vehicle-treated nerves (C), whereas large dystrophic-appearing axons without myelination are commonly present in the CTB-treated nerves (D) at the sciatic level (S2). Scale bar, 2 μm. E, F, Histograms showing distribution of myelinated (E) and unmyelinated dystrophic fibers (F) in vehicle (control)- and CTB-treated nerves at sciatic (S2) level; a marked rightward shift in the distribution of unmyelinated dystrophic axons is seen with CTB treatment (F).
