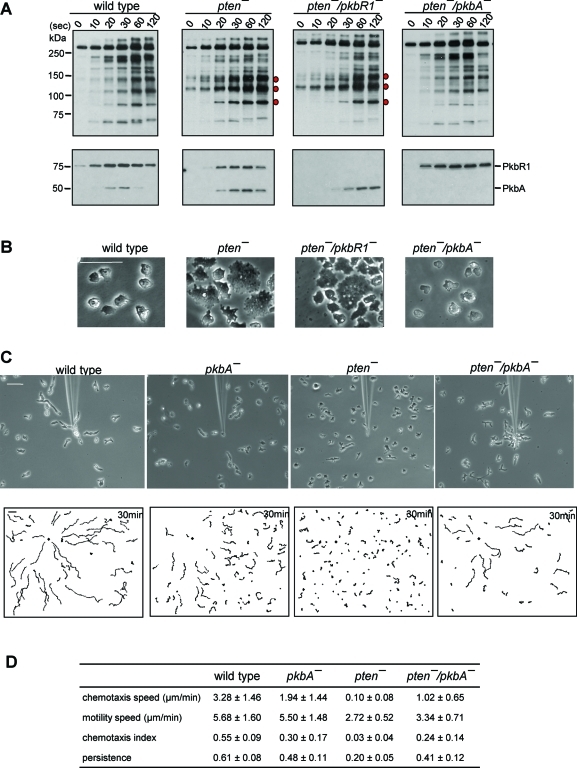
FIGURE 1:
Disruption of PkbA, but not PkbR1, reverses defects in pten- cells. (A) Developed cells were stimulated with 1 μM cAMP and collected at the indicated time points. Upper panels show Western blots using anti–phosphospecific PKB substrate antibodies that recognize R-X-R-X-X-S/T-X-X in a phosphorylation-dependent manner. Lower panels show Western blots using anti–phospho PKC (pan) antibodies that recognize phosphorylation of the activation loop in PkbA and PkbR1. Bands that show increased phosphorylation levels compared with wild-type cells are indicated by red dots. (B) Representative images of cells growing on glass substrates. Bar, 50 μm. (C) Chemotaxis of cells moving toward a micropipette filled with 10 μM cAMP. Cells were observed for 30 min at 30-s intervals. Upper panels show images at 30 min after chemotaxis was initiated. In lower panels, trajectories of the entire recording field are shown. The black diamond indicates the location of the micropipette tip. Bar, 50 μm. (D) Quantification of the chemotaxis movies. Average and standard deviation of at least three movies for each cell line are calculated. See Materials and Methods for definitions of these parameters.