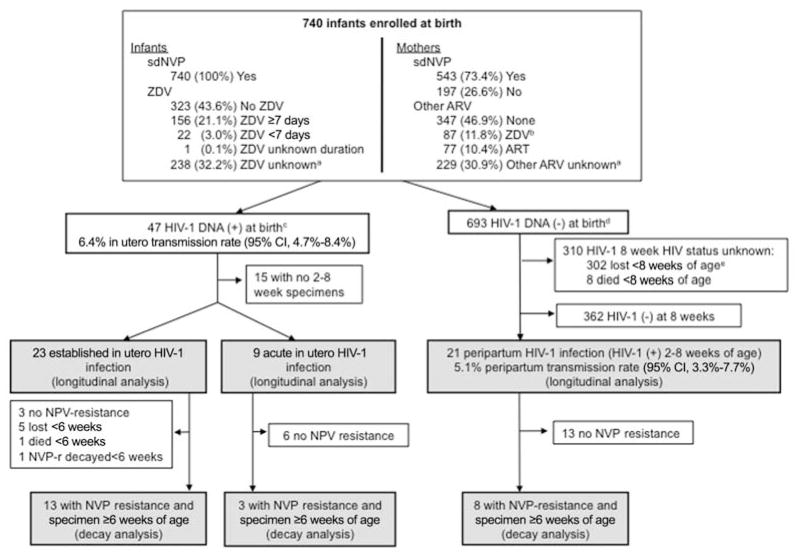
Figure 1.
Infant enrollment, study follow-up, and human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) status through 8 weeks of age. A total of 740 infants born to HIV-1–infected mothers were enrolled in the study during the period June 2005–February 2008. Of the 47 (6.4.%) infected in utero, 32 had follow-up beyond birth and were analyzed for the selection of nevirapine (NVP)–resistant HIV-1 prior to 8 weeks of age (longitudinal analysis), including 23 with established in utero infection (HIV-1 DNA level, >2.4 log10/106 white blood cells in birth specimen) and 9 with acute in utero infection (HIV-1 DNA was less than this threshold at birth and increased by >1 log10 in subsequent specimens). Of these, only 13 and 3 infants with established and acute in utero infection, respectively, had NVP resistance prior to 8 weeks of age and sufficient samples beyond 6 weeks of age for analysis of decay of NVP-resistant HIV-1 (decay analysis). Of the 693 infants with negative HIV-1 DNA at birth, 21 had peripartum HIV-1 infection (HIV-1 DNA positive at 2–8 weeks of age) and were analyzed for detection of NVP-resistant HIV-1 (longitudinal analysis). Of these, 8 had detectable NVP-resistant mutations, and all had sufficient samples for analysis of NVP resistance decay (decay analysis). ART, antiretroviral therapy; ARV, antiretroviral; sdNVP, single-dose NVP; ZDV, zidovudine. aUnknown because mother/infant had no postbirth follow-up visit, when prepartum and postpartum ARVs were ascertained and/or confirmed. bOne mother also received ZDV and lamivudine for 1 week after delivery. cBirth specimens were available for 82%, 93%, 94%, and 96% within day of life 1–5, respectively; includes 2 infants with high concentrations of HIV-1 DNA detected in their first specimen collected at 8 and 11 days of age, suggesting established in utero infection. dIncludes 7 infants without birth specimens who were HIV-1 DNA negative in subsequent specimens. eHIV-1 polymerase chain reaction result was negative for the latest specimen tested.