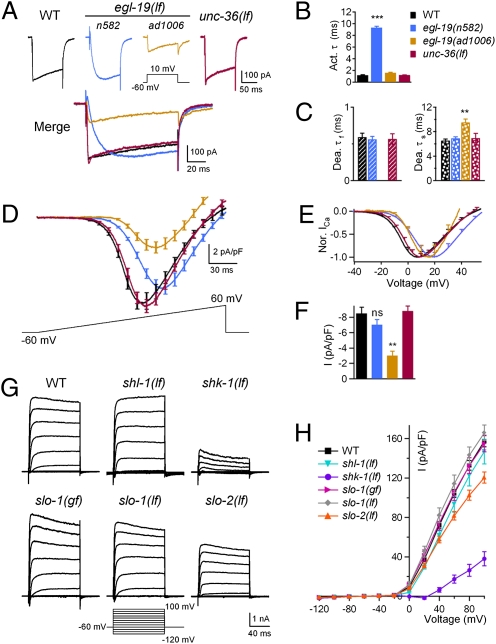
Fig. 3.
lf mutations in L-VGCC/EGL-19 and Kv1/SHK-1 affect the voltage-dependent Ca2+ and K+ currents. (A) Representative voltage-gated Ca2+ currents of WT, egl-19(n582,lf), egl-19(ad1006,lf), and unc-36(lf) mutants. (B) Ca2+ current activation time constants (activation τ) were increased in egl-19(n582,lf) mutants. (C) The fast (Dea. τf) component of Ca2+ current deactivation time constants was abolished, and the slow (Dea. τs) component was delayed in egl-19(ad1006,lf) mutants. (D) Current–voltage (I–V) relationship of VGCC was affected in egl-19(n582,lf) and egl-19(ad1006,lf) but not unc-36(lf). (E) Normalized I–V curve showed that the voltage dependence was shifted by approximately +10 mV in egl-19(n582,lf) and by approximately +5 mV in egl-19(ad1006,lf). (F) The peak Ca2+ current density was decreased approximately threefold in egl-19(ad1006,lf) animals but unaffected in egl-19(n582,lf) and unc-36(lf) mutants. (G and H) K+ current densities showed a significant decrease in shk-1(lf) and a slight reduction in slo-2(lf) mutants at ≥+40 mV. ns, not significant; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; t test against WT. (Error bars: SEM.)