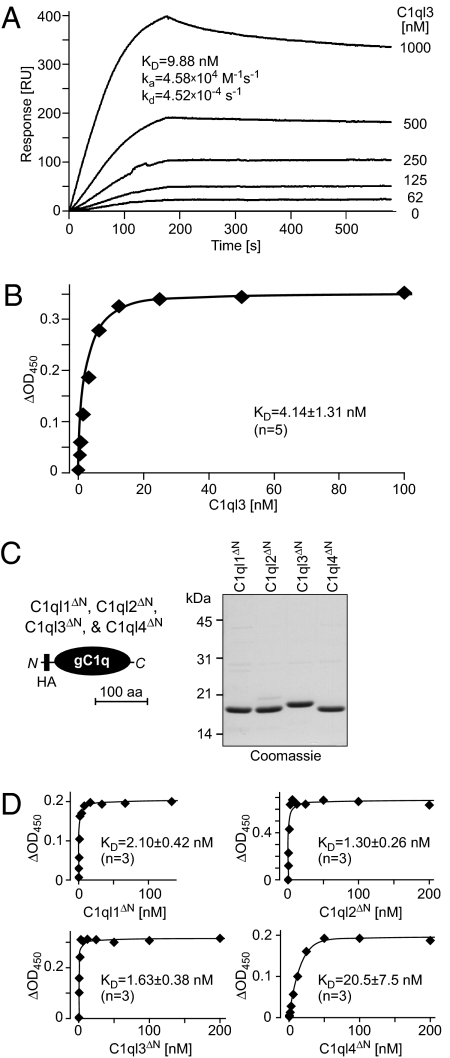
Fig. 3.
Nanomolar affinity of C1ql1, C1ql2, C1ql3, and C1ql4 for BAI3. (A) Surface plasmon resonance measurements. Full-length C1ql3 was injected at the indicated concentrations onto chips containing immobilized IgBAI3-3 or IgC for 180 s, followed by injection of buffer alone. Deduced binding constants are listed in the graph. RU, resonance units. (B) Cell-surface binding measurements with full-length C1ql3 as a ligand. HEK293 cells were transfected with a BAI3 cDNA or mock-transfected, incubated with purified HA-tagged full-length C1ql3 at the indicated concentrations, and fixed. Bound protein was detected with a peroxidase-conjugated antibody against the HA epitope. The signal shown was subtracted for background observed with mock-transfected cells. Data are from a representative experiment independently repeated five times, with Scatchard fits resulting in the indicated binding constant (mean ± SEM). (C) Schematic diagram (Left) and Coomassie blue–stained SDS gel (Right) of recombinant gC1q domains of all four C1ql proteins. gC1q domains were expressed with an N-terminal HA tag as GST-fusion proteins in Escherichia coli, and GST was removed by thrombin cleavage after purification with glutathione-Sepharose. gC1q domains are referred to as C1ql1ΔN–C1ql4ΔN because the N-terminal cysteine sequence and collagen domain were deleted from the C1ql proteins to generate these recombinant domains. (D) Binding curves generated as described in B, but with HA-tagged N-terminally truncated C1ql molecules consisting only of the HA-tagged gC1q domains of the respective proteins. Data shown are from a representative experiment independently repeated three times, with Scatchard fits resulting in the indicated binding constants (mean ± SEM).