Figure 1. Loss of function for Neur causes symmetric division of neural precursor cells.
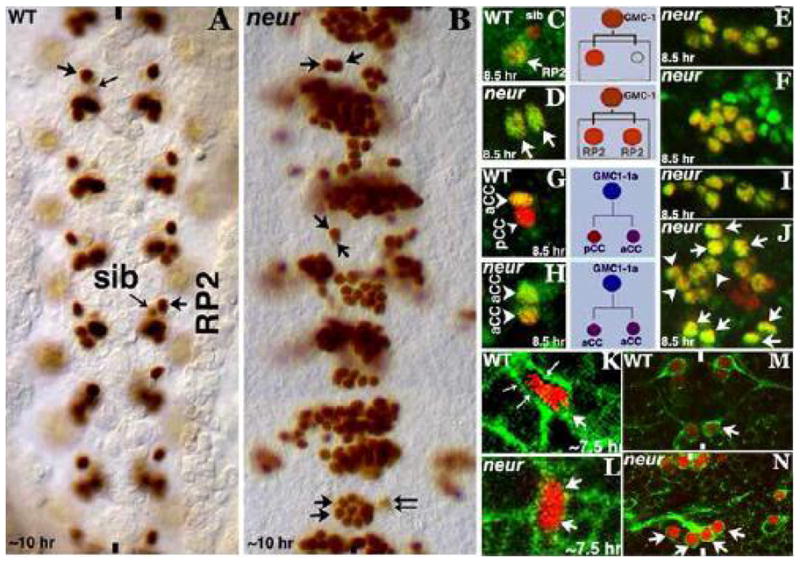
Embryos in panels A and B are stained for Eve, panels C-J are double stained for Eve (Red) and Zfhl (Green), panels in K and L are doubled stained for Eve (Red) and Spectrin (Green), panels M and N are stained for Eve (Red) and 22C10 (MAPIB; Green). Anterior end is up, midline is marked by vertical lines. An RP2 is indicated by an arrow, a sib by a small arrow, and an aCC by an arrowhead, and pCC by a small arrowhead. Two small-long arrows in panel K show the site of GMC-1 (of the RP2/sib lineage) cytokinesis. Panels A and B: Wild type and neur mutant, in the mutant (B), the GMC-1 in a non-neurogenic hemisegment has symmetrically divided into two RP2s (arrows). Note that in the middle segment, one of the duplicated RP2s is smaller than the other. While many hemisegments have multiple RP2s (arising from both symmetrical division and an earlier neurogenic defect, hemisegments with both RP2s and sibs can also be seen, bottom segment in panel B). Panel C: wild type, only a mature RP2 expresses Zfhl but not a sib. Panel D: Both the daughters of a GMC-1 in neur have Eve and Zfhl expression indicating their RP2 identity. Panels E and F: Even in those hemisegments where there is a neurogenic effect, only Eve and Zfhl positive RP2s are observed but not sib indicating symmetrical division of multiple GMCs. Panel G: Wild type, only aCC has both Eve and Zfhl, pCC has only Eve. Panel H: Both the daughters of GMC of the aCC/pCC have Eve and Zfhl although the transformed aCC has a lower expression of Zfhl compared to the bona fide aCC. Panels I and J: Many more aCCs are seen in the mutant embryo in those neurogenic hemisegments (arrowheads). Panel K: Wild type, a GMC-1 is unequally dividing into a larger RP2 and a smaller sib. Panel L: A GMC-1 in neur mutant is dividing equally into two RP2s. Panel M: Wild type, showing RP2s sending out their projection to the ISN bundle. Panel N: Duplicated RP2s with aberrant projections in the neur mutant.
