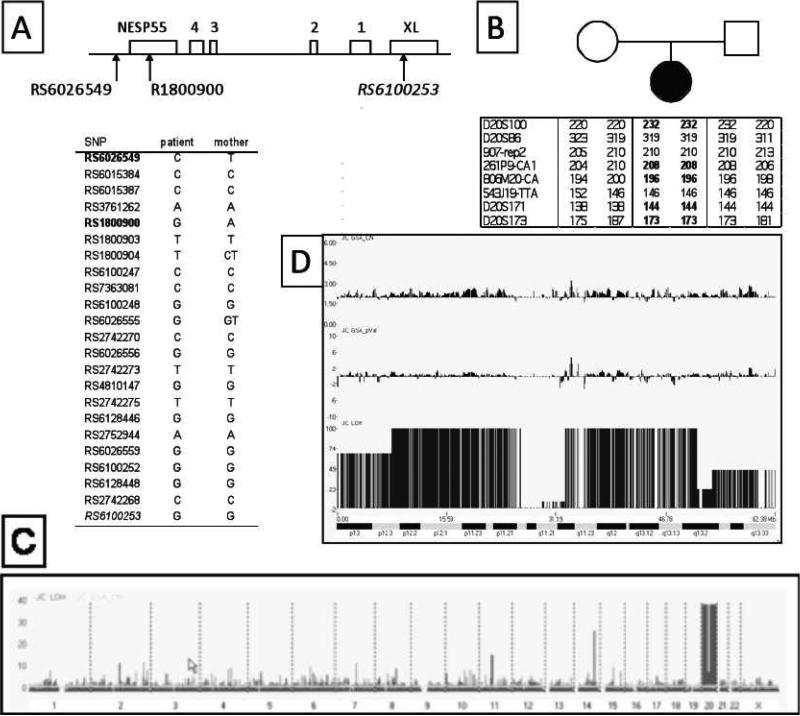
Figure 1. Identification of a paternal UPD of entire chromosome 20 in the index patient.
A. Analysis of SNPs within the upstream region of GNAS. Genomic DNA from the patient and her mother were genotyped for 23 SNPs clustered within the centromeric portion of GNAS that includes exons NESP55, XL, and exons 1-4 of the antisense transcript, revealing two discordant SNPs (bold) located upstream or within NESP55.
B. Analysis of polymorphisms in the chromosomal region comprising GNAS. The patient and her parents were also genotyped for microsatellites within the telomeric end of chromosome 20q, demonstrating a loss of the maternal allele for five of eight informative markers (bold).
C. 100K SNP Chip analysis of leukocyte genomic DNA. Genome-wide analysis with LOH probability (black) and the copy number (CN; grey) were plotted together.
D. Analysis of chromosome 20. The probability of LOH (JC LOH) is significantly elevated, while the copy number (JC GSA_CN) and the p-value (JC GSA_pVal) for the same chromosome are not different from other chromosomes. The gap represents the centromeric region. The cytobands of chromosome 20 are displayed below. Analysis was performed concomitantly on DNA samples from the patient and her parents, but the results shown here were obtained with DNA from the patient. The parental DNA did not reveal any abnormalities (data not shown).