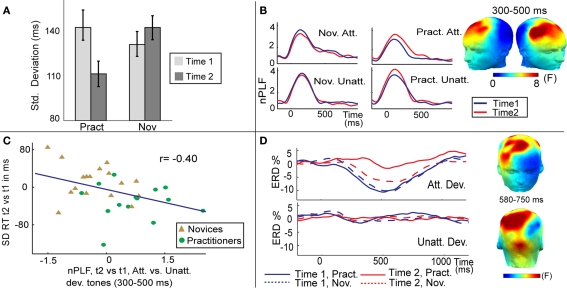
Figure 1.
Effects of FA meditation. (A) Intensive mental training reduced intra-individual variability of behavioral performance. Average SD of reaction time in response to target (attended deviant) tones, separately for each session (time 1, time 2) and group [practitioners (Pract), novices (Nov)]. (B) Intensive mental training increased trial-to-trial consistency of brain responses to attended deviant tones. The scalp maps show the spatial distribution of the mental training-related increase in theta-band (4–7 Hz) phase consistency (indexed by normalized PLF) to target tones, as indexed by a three-way interaction between group, session, and condition (attended, unattended deviant tones). F values are averaged between 300 and 500 ms. The time course of normalized PLF values averaged across the electrodes sites showing this significant three-way interaction is shown separately for each group, session, and attended (Att) and unattended (Unatt) deviant tones. Note that the observed increase in phase consistency to attended deviant tones over time was only observed for the practitioner group. (C) The correlation plot shows that the observed change in the trial-to-trial variability of brain responses predicted the observed behavioral change in the trial-to-trial variability of the RT. (D) Mental training selectively reduced cognitive effort as indexed by ERD. Time course of the ERD for attended and unattended deviant tones (Dev.) shown for the practitioners and novices separately. The scalp maps show the spatial distribution of the mental training-related decrease in beta-band (13–30 Hz) ERD to attended vs. unattended deviant tones [three-way interaction between group, session, and condition]. F values are averaged between 580 and 750 ms. Figure is adopted from Lutz et al. (2009).