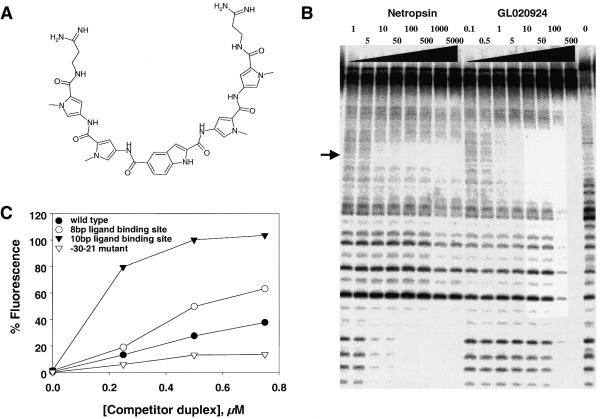
Figure 4.
Biochemical analysis of the DNA-binding properties of GL020924. (A) The chemical structure of GL020924. (B) DNase I footprint of GL020924 on DNA. Increasing concentrations of either netropsin or GL020924 (amounts are indicated in nM above their respective lanes) were assayed by DNase I footprinting as described in Materials and Methods. The DNA sequence of the oligonucleotide is as described in Materials and Methods and the footprinted region, TATTAATA, is indicated by the arrow. (C) Various cyclin D1 promoter sequences were used to compete with the fluorescent/DABCYL indicator DNA duplex (5′-fluorescein-CTTTATTATTTT and 3′-DABCYL-AAAATAATAAAG) for GL020924 binding. Competitor duplex DNAs were: wild-type cyclin D1 sequence, 5′-GGGAGTTTTGTTGAAGTTG-3′ (solid circles); –30 to –21 mutant sequence, 5′-GGTCTGGGATCCGAAGTTG-3′ (open circles); 10 bp AT-rich site-containing sequence, 5′-GGGAGTTTTTTTTAAGTTG-3′ (solid triangles); 8 bp AT-rich site-containing sequence, 5′-GGGAGTTTTAAAAGAGTTG-3′ (open triangles); mutagenized bases are underlined, GL020924 concentration was 1000 nM in all samples.