Abstract
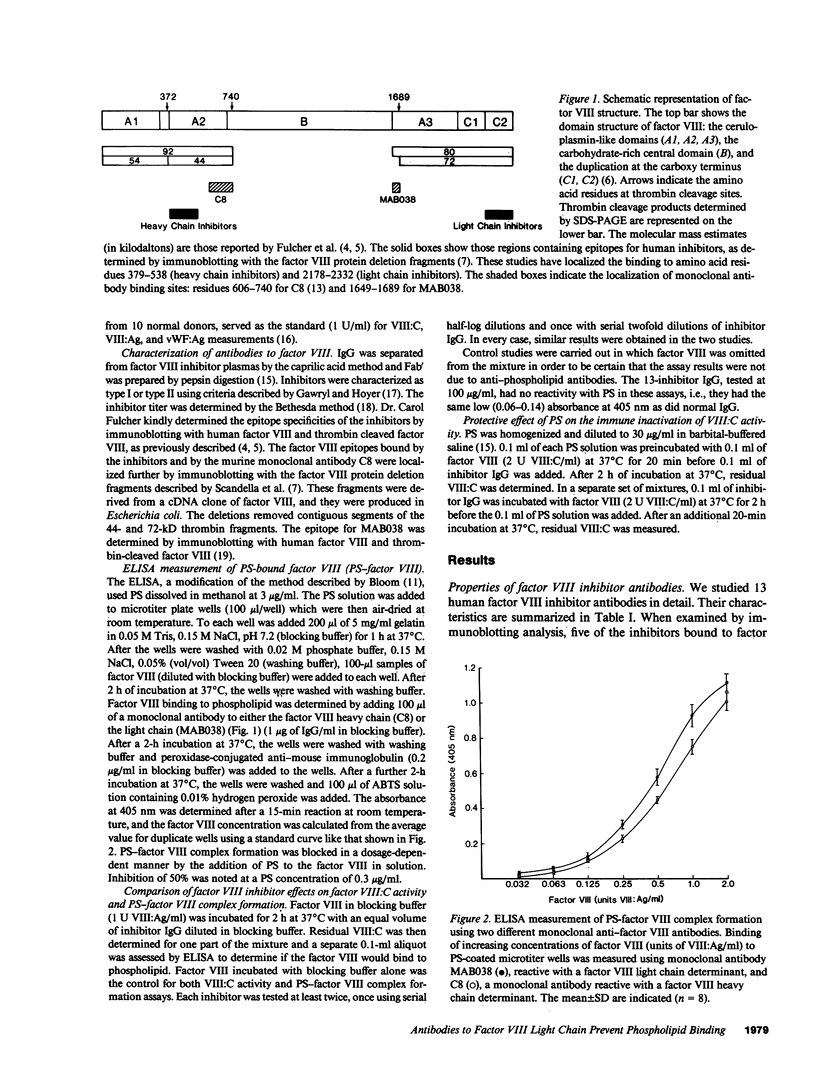
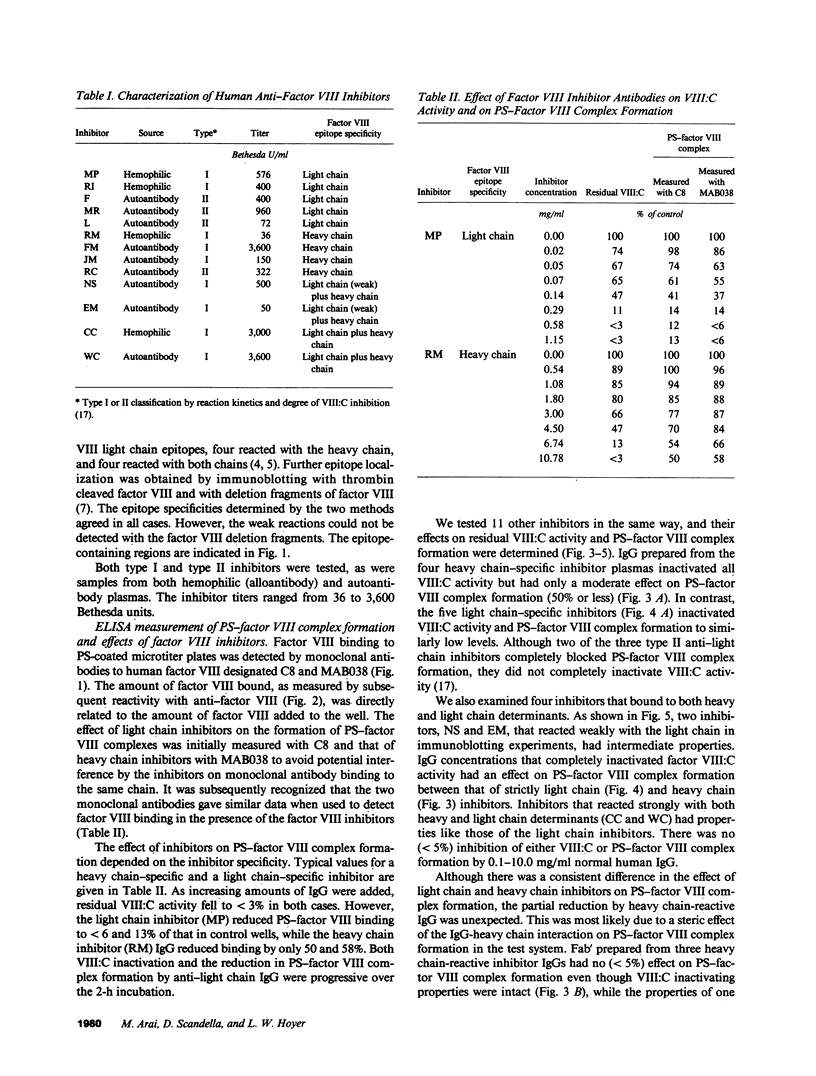
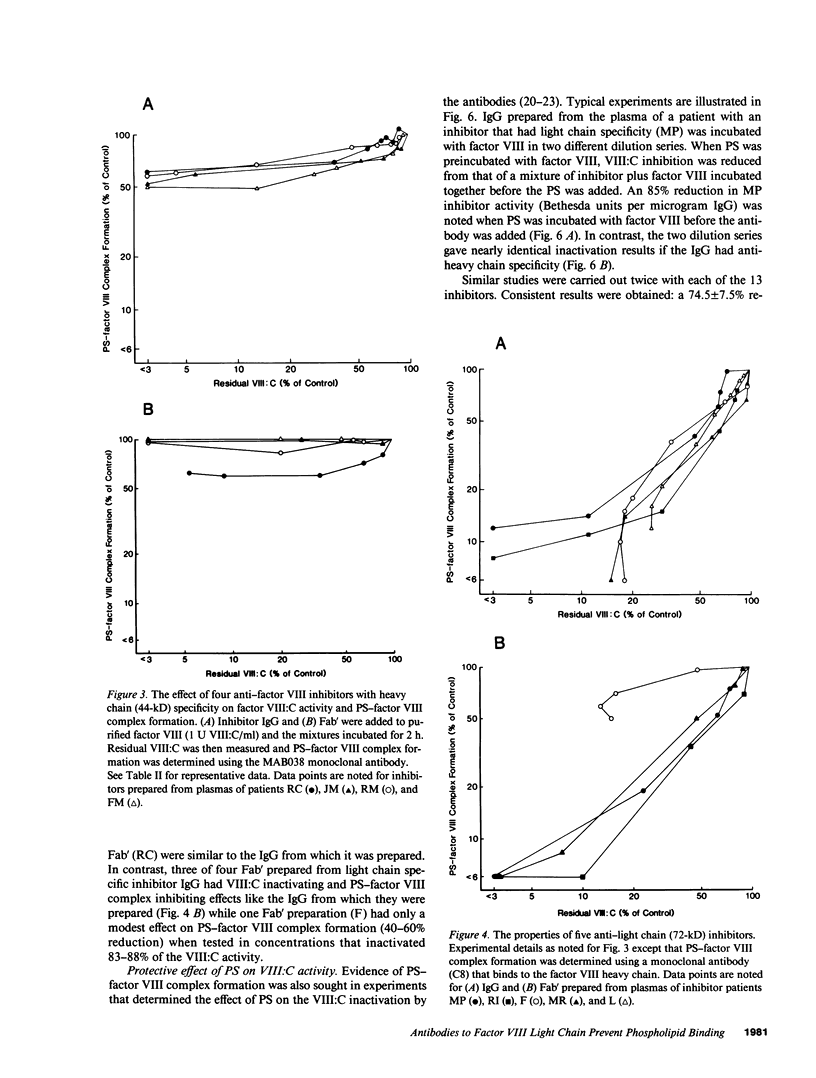
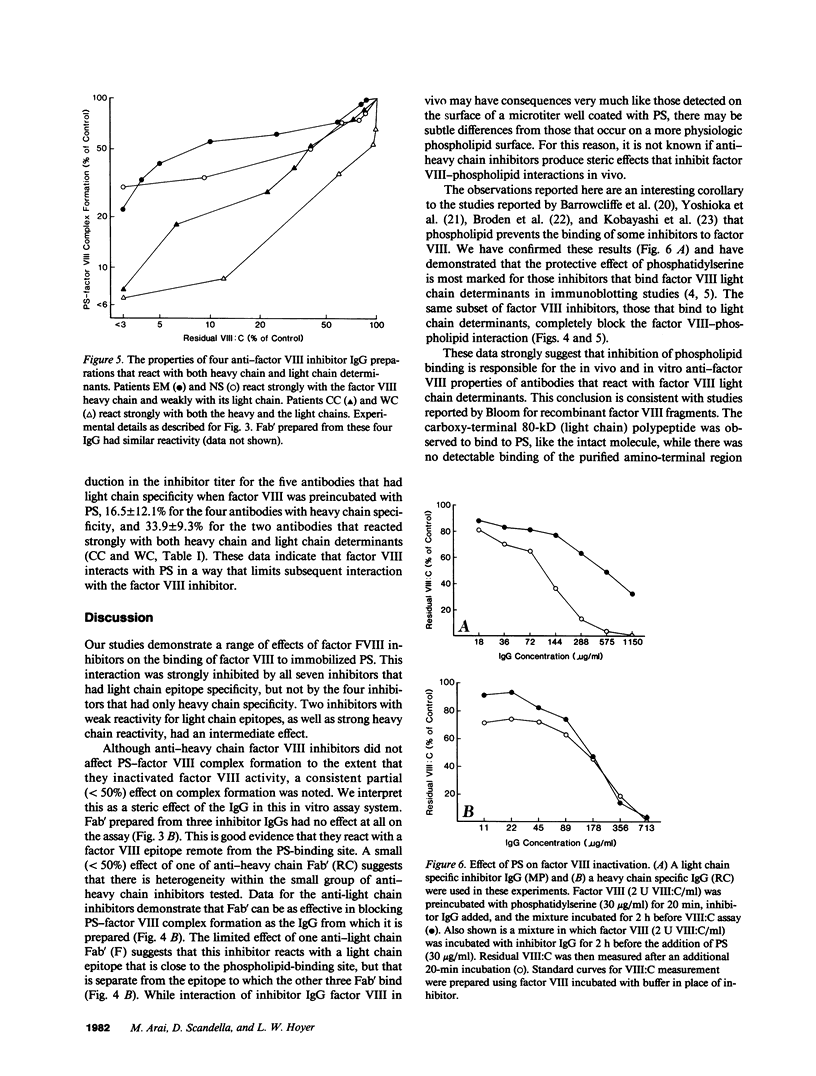
Most antibodies to factor VIII have recently been shown to react with discrete regions of the factor VIII light chain (within the C2 domain) and/or the factor VIII heavy chain (within the amino-terminal segment of the A2 domain). The mechanism by which these antibodies, usually designated "factor VIII inhibitors," interfere with factor VIII function has been examined by determining their effect on factor VIII binding to a phospholipid. Factor VIII-phosphatidylserine binding was prevented by all seven factor VIII inhibitors that had strong factor VIII light chain reactivity and reduced by two inhibitors with weak anti-light chain reactivity. None of four inhibitors with heavy chain reactivity prevented factor VIII-phosphatidylserine interaction, though a partial reduction (less than 50%) was noted for the intact IgG preparations. However, when Fab' fragments were substituted, no detectable reduction in factor VIII-phosphatidylserine binding was noted for the anti-heavy chain inhibitors and complete inhibition was retained by the anti-light chain inhibitors. These data suggest that a subset of factor VIII inhibitors, those that bind to light chain determinants, inactivate factor VIII by preventing its effective interaction with phospholipid.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson L. O., Brown J. E. Interaction of factor VIII-von Willebrand Factor with phospholipid vesicles. Biochem J. 1981 Oct 15;200(1):161–167. doi: 10.1042/bj2000161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antonarakis S. E., Youssoufian H., Kazazian H. H., Jr Molecular genetics of hemophilia A in man (factor VIII deficiency). Mol Biol Med. 1987 Apr;4(2):81–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRECKENRIDGE R. T., RATNOFF C. D. Studies on the nature of the circulating anticoagulant directed against antihemophilic factor: with notes on an assay for anthemophilic factor. Blood. 1962 Aug;20:137–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrowcliffe T. W., Kemball-Cook G., Gray E. Binding to phospholipid protects factor VIII from inactivation by human antibodies. J Lab Clin Med. 1983 Jan;101(1):34–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom J. W. The interaction of rDNA factor VIII, factor VIIIdes-797-1562 and factor VIIIdes-797-1562-derived peptides with phospholipid. Thromb Res. 1987 Nov 15;48(4):439–448. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(87)90401-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodén K., Brown J. E., Carton C., Andersson L. O. Effect of phospholipid on factor VIII coagulant activity and coagulant antigen. Thromb Res. 1983 Jun 15;30(6):651–660. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(83)90274-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster P. A., Fulcher C. A., Houghten R. A., de Graaf Mahoney S., Zimmerman T. S. Localization of the binding regions of a murine monoclonal anti-factor VIII antibody and a human anti-factor VIII alloantibody, both of which inhibit factor VIII procoagulant activity, to amino acid residues threonine351-serine365 of the factor VIII heavy chain. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jul;82(1):123–128. doi: 10.1172/JCI113559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher C. A., Roberts J. R., Holland L. Z., Zimmerman T. S. Human factor VIII procoagulant protein. Monoclonal antibodies define precursor-product relationships and functional epitopes. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jul;76(1):117–124. doi: 10.1172/JCI111933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher C. A., de Graaf Mahoney S., Roberts J. R., Kasper C. K., Zimmerman T. S. Localization of human factor FVIII inhibitor epitopes to two polypeptide fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7728–7732. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher C. A., de Graaf Mahoney S., Zimmerman T. S. FVIII inhibitor IgG subclass and FVIII polypeptide specificity determined by immunoblotting. Blood. 1987 May;69(5):1475–1480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gawryl M. S., Hoyer L. W. Inactivation of factor VIII coagulant activity by two different types of human antibodies. Blood. 1982 Nov;60(5):1103–1109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill F. M. The natural history of factor VIII inhibitors in patients with hemophilia A. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1984;150:19–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. L., Mann K. G. The interaction of bovine factor V and factor V-derived peptides with phospholipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6503–6508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer L. W., Gawryl M. S., de la Fuente B. Immunochemical characterization of factor VIII inhibitors. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1984;150:73–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer L. W. Immunologic studies of antihemophilic factor (AHF, factor VIII). IV. Radioimmunoassay of AHF antigen. J Lab Clin Med. 1972 Dec;80(6):822–833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane W. H., Davie E. W. Cloning of a cDNA coding for human factor V, a blood coagulation factor homologous to factor VIII and ceruloplasmin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6800–6804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemball-Cook G., Barrowcliffe T. W. Factor VIII concentrates contain factor VIII procoagulant antigen bound to phospholipid. Br J Haematol. 1986 Jul;63(3):425–434. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1986.tb07519.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi I., Lamme S., Nilsson I. M. The interaction between factor VIII clotting antigen and phospholipids in genetic variants of hemophilia and von Willebrand's disease. Thromb Res. 1984 Jul 1;35(1):65–75. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(84)90313-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnaswamy S., Mann K. G. The binding of factor Va to phospholipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5714–5723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lajmanovich A., Hudry-Clergeon G., Freyssinet J. M., Marguerie G. Human factor VIII procoagulant activity and phospholipid interaction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Nov 18;678(1):132–136. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(81)90056-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarchick J., Hoyer L. W. Immunoradiometric measurement of the factor VIII procoagulant antigen. J Clin Invest. 1978 Nov;62(5):1048–1052. doi: 10.1172/JCI109209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letter: A more uniform measurement of factor VIII inhibitors. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1975 Dec 15;34(3):869–872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman D. D., Kaufman R. J. Proteolytic requirements for thrombin activation of anti-hemophilic factor (factor VIII). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2429–2433. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotblat F., O'Brien D. P., O'Brien F. J., Goodall A. H., Tuddenham E. G. Purification of human factor VIII:C and its characterization by Western blotting using monoclonal antibodies. Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 30;24(16):4294–4300. doi: 10.1021/bi00337a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scandella D., DeGraaf Mahoney S., Mattingly M., Roeder D., Timmons L., Fulcher C. A. Epitope mapping of human factor VIII inhibitor antibodies by deletion analysis of factor VIII fragments expressed in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):6152–6156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.6152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vehar G. A., Keyt B., Eaton D., Rodriguez H., O'Brien D. P., Rotblat F., Oppermann H., Keck R., Wood W. I., Harkins R. N. Structure of human factor VIII. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):337–342. doi: 10.1038/312337a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshioka A., Peake I. R., Furlong B. L., Furlong R. A., Giddings J. C., Bloom A. L. The interaction between factor VIII clotting antigen (VIIICAg) and phospholipid. Br J Haematol. 1983 Sep;55(1):27–36. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1983.tb01221.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


