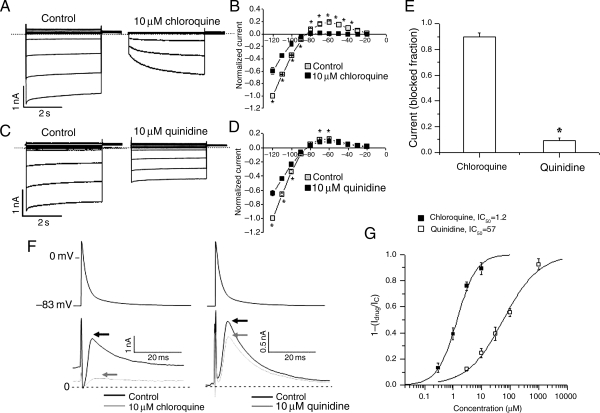
Figure 3.
Effects of chloroquine and quinidine on IK1. Currents in response to 4 s pulses from a holding potential of −80 mV to test potentials from −120 mV to −20 mV, applied at 10 mV increments in HEK-293 cells transfected with Kir2.1 in the absence and presence of 10 μM chloroquine (A) or 10 μM quinidine (C). Scale: 2 s; 1 nA, the dashed lines define the zero current levels. IV curves of currents at the end of pulses are normalized to the current at −120 mV, obtained under control conditions (n = 5 cells, *P< 0.05). Chloroquine (B) reduces both the inward and outward components of IK1. Quinidine (D) reduces the inward component of IK1 but has a modest effect on the outward current. (E) The fraction of blocked outward current at −60 mV by chloroquine was 0.90 ± 0.03 vs. 0.09 ± 0.02 in response to quinidine (n= 5, *P< 0.01). (F) AP voltage clamping in HEK-293 cells transfected with Kir2.1. Top, mouse left ventricular AP. Bottom, IK1 current profile in response to the AP voltage clamp with 10 µM chloroquine or quinidine. Chloroquine reduces the maximum current (indicated by arrows). Quinidine has a modest effect. (G) Dose response curve of the fractional blocked peak outward current in response to the AP voltage clamp with chloroquine and quinidine. Solid lines are Hill equation best fits. IC50: chloroquine = 1.2 ± 0.2, quinidine = 57 ± 3.8 μM.