Figure 2. Anatomy of feedforward and feedback connections between the LGN and visual cortex (V1).
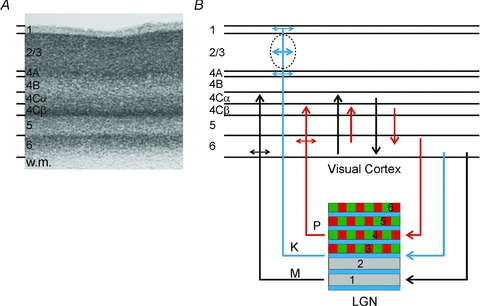
A, Nissl-stained section of V1 from the macaque monkey. Corticogeniculate neurones are located exclusively in layer 6. (w.m., white matter.) B, organization of connections between the LGN and V1. The magnocellular layers of the LGN (1 and 2) are shown in grey, the parvocellular layers (3, 4, 5 and 6) are shown in green and red, the koniocellular layers are located below each of the magnocellular and parvocellular layers and are shown in blue. Magnocellular LGN axons (M) terminate in layers 4Cα and lower layer 6, parvocellular LGN axons (P) terminate in layers 4Cβ and upper layer 6, koniocellular LGN axons (K) terminate in layer 4A, the cytochrome oxidase rich blobs and layer 1. The intrinsic connections in V1 maintain the magno- and parvocellular divisions of layers 4C and 6. Neurones in layer 6 of cortex provide feedback to the LGN. Neurones in the upper third of layer 6 project exclusively to the parvocellular LGN layers. Neurones in the lower third of layer 6 project primarily to the magnocellular layers and perhaps the koniocellular layers.
