FIGURE 2.
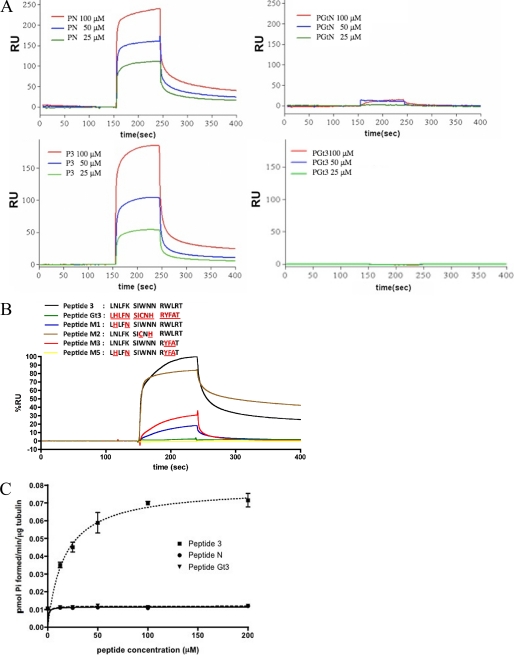
Gαs-derived peptides specifically interact with tubulin. A, sensorgrams from surface plasmon resonance analysis show the mass of indicated peptides bound to tubulin over time (in resonance units (RU)). Varying concentrations of Gαs-derived N-terminal peptide (peptide N (PN)), Gαt-derived N-terminal peptide (PGtN), Gαs-derived α3–β5 peptide (P3), and Gαt-derived α3–β5 peptide (PGt3) were used. n = 3 experiments. B, four variants of P3 (M1, M2, M3, and M5) were synthesized by replacing Gαs residues with homologous residues in transducin (indicated in red). The binding of 100 μm peptides to immobilized tubulin is shown. C, activation of tubulin GTPase by a Gαs-derived peptide (P3). P3 increased tubulin GTPase in a dose-dependent, saturable fashion. Vmax = 0.070 pmol of Pi formed/min/μg of tubulin, and EC50 = 24 μm. Peptide N and peptide Gαt3 have no measurable effect on tubulin GTPase. All peptides are listed in supplemental Table 2.