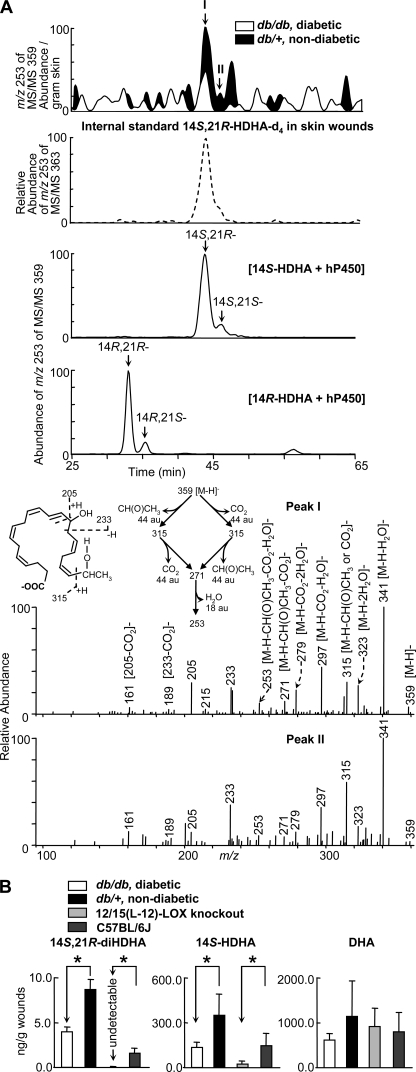
FIGURE 1.
Formation of 14S,21R-diHDHA was suppressed in skin wounds in diabetic db/db mice compared with nondiabetic db/+ mice. Wounded skin was harvested from mice immediately following sacrifice at day 1 after the splinted excisional wounding was performed. A, overlay ChiralPak-IA-based chiral LC-MS/MS chromatograms (top panels) of wounds of db/+ (solid black) and db/db (open line) mice, and spectra (nonwide band) (bottom two panels) of peak I and peak II found in wounds of db/+ mice. For comparison, the ion abundance of each selected MS/MS ion chromatogram was divided by the extraction recovery of the stable deuterated internal standard 14S,21R-diHDHA-d4 added to the sample and then normalized per g of skin. The 2nd panel is a selected ion chromatogram at m/z 253 of MS/MS 363 for internal standard 14S,21R-diHDHA-d4 added to and extracted from skin wounds. This deuterated compound was added to skin wounds collected from mice and used as the internal standard for the quantification of 14S,21R-diHDHA (see details under “Experimental Procedures”). Chromatograms of 14S,21R-diHDHA and 14S,21S-diHDHA (generated from 14S-HDHA by h-P450) as well as 14R,21S-diHDHA and 14R,21R-diHDHA (generated from 14R-HDHA by h-P450) are shown in the 3rd and 4th panels, respectively. B, quantification of 14S,21R-diHDHA, 14S-HDHA, and DHA in wounds of db/+ (solid black), db/db (open bar), 12/15-LOX-knock-out mice (light gray), and C57BL/6J mice (dark gray) via ChiralPak-IA-based chiral LC-MS/MS using stable deuterated internal standards. Results are mean ± S.E. (n = 3). *, p < 0.05 compared with control.