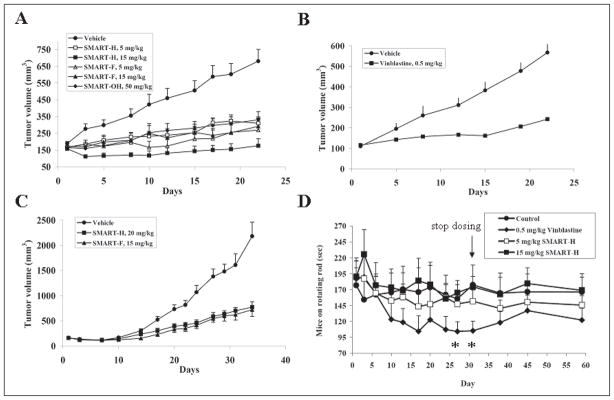
Figure 4.
In vivo anti-cancer efficacy and neurotoxicity of SMART compounds. (A) SMARTs efficacy for PC-3 prostate tumor xenografted on nude mice (n = 6–8). (B) Vinblastine efficacy for PC-3 prostate tumor xenografted on nude mice (n = 8). This served as the positive control. (C) In vivo efficacy of SMART-H and SMART-F in nude mice bearing A375 melanoma xenografts (n = 10). Nude mice were inoculated 2.5 × 106 PC-3 or A375 cells and dosed i.p. daily (SMART compounds) and q2d (vinblastine) after tumor formation (150–200 mm3). Each point represents mean tumor volume for animals in each group. (D) In vivo neurotoxicity (rotarod test) of SMART-H in ICR mice (n = 7 or 8). SMART-H (5 and 15 mg/kg), vinblastine (0.5 mg/kg) and vehivle were given i.p. daily, and vinblastine was used as the positive control. The dosing was stopped on day 31. *, p < 0.05. Bars, SE