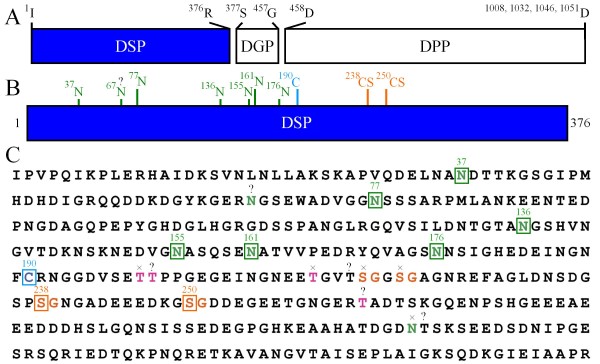
Figure 7.
Porcine Dsp posttranslational modification sites. A: Diagram showing the three regions (Dsp, Dgp, and Dpp) of porcine Dspp. B: Diagram showing N and O-linked glycosylation sites identified in this study. Among the eight asparagines in the appropriate context for glycosylation, six were determined to be glycosylated (Asn37, Asn77, Asn136, Asn155, Asn161, Asn176). The glycosylation status Asn67 was not determined. Asn315 was shown to not be glycosylated, possibly due to an O-glycosylation of Thr316. In porcine Dsp, it was shown that the N-glycosylations contain, on average, one sialic acid, in the form of N-acetylneuraminic acid, per N-glycosylation. Ser238 and Ser250 were determined to be GAG attachment sites, with the GAG attachments being comprised of chondroitin 6-sulfate and chondroitin 4-sulfate in a ratio of 7 to 3. O-glycosylations were suggested by blank cycles at Thr200, Thr216, and Thr316 in samples that were positive for glycosylation by the phenol sulfuric acid assay and eluted early from a size-exclusion column, but no direct evidence for O-glycosylation was obtained and the conclusion that these residues are glycosylated should be considered tentative.