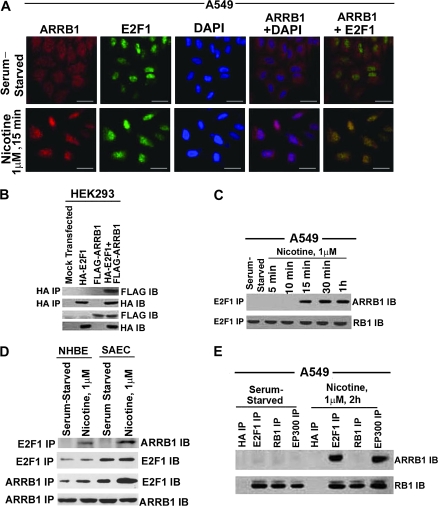
Figure 3.
Effect of nicotine on association between E2F1 and ARRB1 in human non–small cell lung cancer cells. A) Serum-starved A549 were treated with 1 μM nicotine for 15 minutes, and localization of ARRB1 and E2F1 was analyzed by double-immunoflourescence staining followed by confocal microscopy (×630 magnification, scale bar = 5 μm). The cells were counterstained with the nuclear marker, 4′6-diamidino-2-phenylindole. Overlay of the images show yellow spots indicating colocalization in the bottom right panel. B) Effect of overexpression of pcDNA3-FLAG-rat ARRB1 (wild type) and pcDNA3-HA-E2F1 in HEK293 cells. HEK293 cells were transfected with the above plasmids, and the physical interaction between ARRB1 and E2F1 was analyzed 24 hours after transfection by immunoprecipitation with mouse anti-HA antibody followed by immunoblotting using mouse anti-FLAG antibody. In addition, immunoblot analysis was done for FLAG and HA expression. C) Real-time kinetics of ARRB1–E2F1 interaction upon nicotine treatment of A549 cells. Serum-starved A549 cells were treated with 1 μM nicotine for 15 minutes, 30 minutes, and 1 hour, and the physical interaction between ARRB1 and E2F1 was analyzed by immunoprecipitation–immunoblot assay. Furthermore, the E2F1 immunoprecipitates were immunoblotted for RB1 to demonstrate equivalent amount of E2F1. D) Effect of nicotine on the association of ARRB1 and E2F1 in normal lung epithelial cells, NHBEs and SAECs. Quiescent NHBEs and SAECs were treated with 1 μM nicotine for 15 minutes, and the physical interaction between ARRB1 and E2F1 was analyzed by immunoprecipitation–immunoblot analysis. Furthermore, the E2F1 and ARRB1 immunoprecipitates were immunoblotted with E2F1 and ARRB1 to demonstrate equivalent amounts of protein. E) Effect of nicotine on binding of ARRB1 to E2F1, RB1 and EP300. Serum-starved A549 cells were treated with 1 μM nicotine for 2 hours. The binding of ARRB1 to E2F1, EP300, and RB1 was analyzed by immunoprecipitation–immunoblotting experiment. Immunoprecipitation with anti-mouse HA antibody was used as the negative control for the experiment. The above-mentioned immunoprecipitates were immunoblotted for RB1 protein. All the immunofluorescence and immunoprecipitation–immunoblotting experiments are representative of two independent experiments. IB = immunoblot; IP = immunoprecipitation.