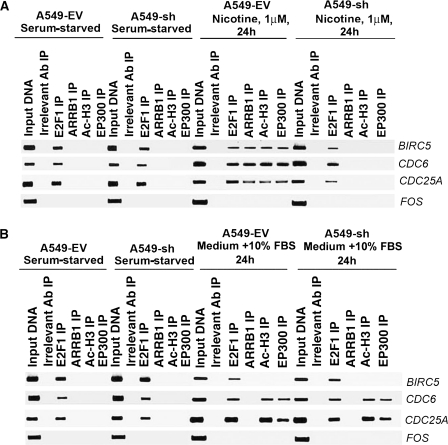
Figure 5.
Effect of suppression of ARRB1 on nicotine-induced vs serum-induced association of E2F1, ARRB1, Ac-H3, and EP300 with E2F-1 responsive promoters. A) Effect of nicotine on the binding of E2F1, ARRB1, Ac-H3, and EP300 with BIRC5, CDC6, and CDC25A promoters in A549-EV and A549-sh cells. Serum-starved A549-EV and A549-sh cells were treated with 1 μM nicotine for 24 hours, and the association of E2F1, ARRB1, Ac-H3, and EP300 with BIRC5, CDC6, and CDC25A promoters was assessed by chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assays. FOS promoter was used as a negative control. B) Effect of serum (medium containing 10% FBS) on the association of E2F1, ARRB1, Ac-H3, and EP300 with BIRC5, CDC6, and CDC25A promoters in A549-EV and A549-sh cells. Serum-starved A549-EV and A549-sh cells were incubated with medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum for 24 hours, and the association of E2F1, ARRB1, Ac-H3, and EP300 with BIRC5, CDC6, and CDC25A promoters was examined by ChIP assays. FOS promoter was used as a negative control. Rabbit anti-mouse IgG was used as the irrelevant antibody for all ChIP reactions. The input lane represents one-fifth of the precleared chromatin used in each ChIP reaction. The results presented in this figure are representative of two independent ChIP assays. Ab = antibody; IP = immunoprecipitation.