Fig. 14.
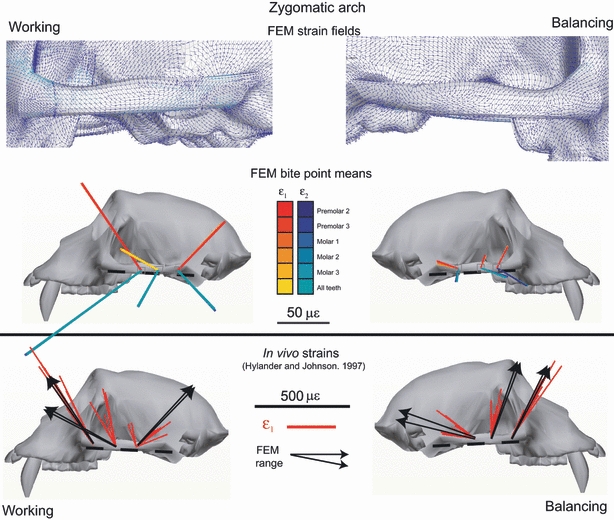
Strain vector plots of in vivo and FEM strain data collected from the zygomatic arch. The in vivo data are from Hylander & Johnson (1997a,b).; The top figure shows the strain field of maximum principal strain orientations at the centroid of each element. The second figure illustrates in silico data from corresponding ‘gage sites’ on the model. For the in silico data, each line is a vector representing the mean orientation and magnitude of maximum (ε1) (red to yellow) and minimum (ε2) (blue to green) principal strains from all the elements at the gage site. Note that the variance among the vectors from the in silico gage sites is due to variation in bite point, and the variance among vectors from in vivo gage sites is due to variation in magnitude and location of bite force, joint reaction forces and muscle forces. The third row illustrates strain vector plots of in vivo strain data from the zygomatic arch reported in Tables 1 and 4 of Hylander & Johnson (1997a,b);. These strain orientations are calculated relative to a horizontal plane passing through the zygomatic arches. The black arrows on the in vivo plots represent the extremes of the ranges of the mean ε1 orientations from the in silico‘gage sites’.
