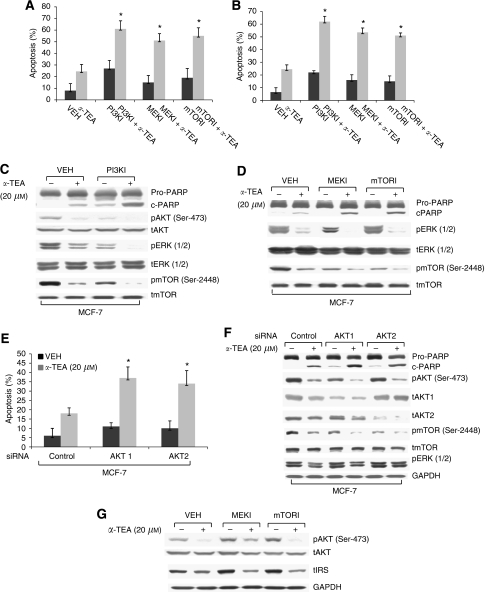
Figure 5.
Inhibitors of PI3K, MEK/ERK, mTOR, as well as siRNAs to AKT1 and AKT2 enhance α-TEA-induced apoptosis. (A and B) HCC-1954 and MCF-7 cells were treated with 1 μM PI3K inhibitor wortmannin (PI3KI), 10 μM MEK inhibitor U01260 (MEKI), or 50 nM mTOR inhibitor rapamycin (mTORI) plus 10 and 20 μM of α-TEA for 18 h, respectively. Apoptosis was determined by Annexin V/PI staining. (C and D) Protein levels of cleaved PARP, pAKT (Ser-473), pERK1/2, and pmTOR (Ser-2448) as well as levels of total AKT, ERK1/2, and mTOR were determined by western blot analyses in MCF-7 cells treated with the three inhibitors plus α-TEA. (E) MCF-7 cells transfected with siRNAs to AKT1, AKT2, or control was treated with 20 μM α-TEA for 18 h. Apoptosis was determined by Annexin V/PI staining. (F) Protein levels of cleaved PARP, pAKT (Ser-473), pmTOR (Ser-2448), pERK1/2, and levels of total AKT1, AKT2, and mTOR were determined by western blot analyses. Levels of GAPDH served as lane controls. (G) MCF-7 cells treated with 10 μM MEK inhibitor U01260 (MEKI) or 50 nM mTOR inhibitor rapamycin (mTORI) plus 20 μM of α-TEA for 18 h. Protein levels of pAKT (Ser-473), AKT, IRS-1, and GAPDH were determined by western blot analyses. Data in (C, D, F, and G) are representative of two separate experiments. Data in (A, B, and E) are presented as mean±s.d. of three independent experiments. *Significantly different from control (P<0.05).