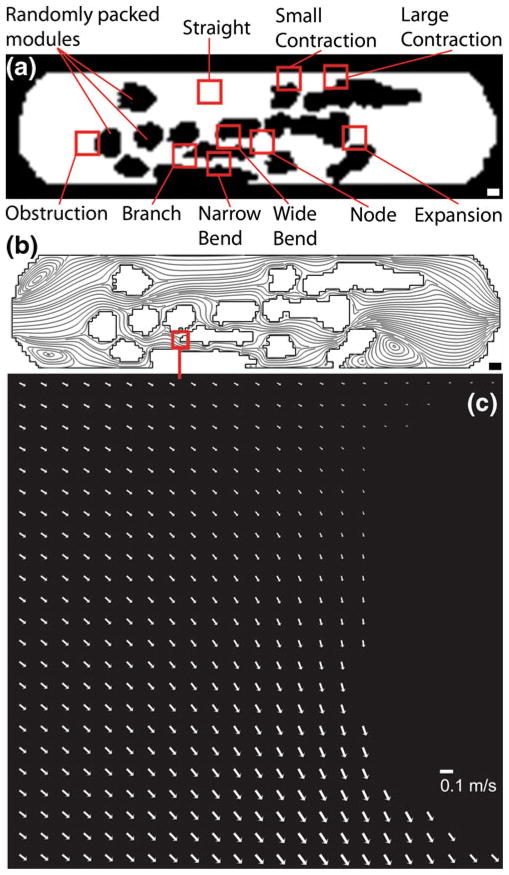
Fig. 3.
The network of channels found in the modular construct (Fig. 1) was reproduced in a microfluidic chamber. (a) Randomly packed modules appear black and act as obstructions to flow. The white region is open and lined with a monolayer of endothelial cells. White scale bar=1000 μm (b) Nine regions of interest, 460 μm×460 μm (boxes not to scale), were selected based on their shape and flow characteristics, the latter determined by their streamlines via computational modeling. Black scale bar= 1000 μm (c) PIV-based arrow plot of flow through the branch region of the microfluidic chamber operating at a flow rate of 11 mL min−1 (τ*, the average shear stress, was 15.6 dyn cm−2). Scale bar=0.1 m s−1