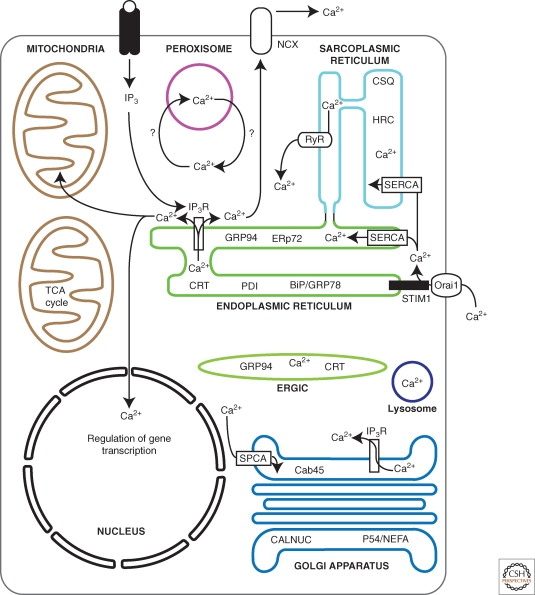
Figure 1.
Organellar Ca2+ buffering and intracellular Ca2+ dynamics. Ca2+ is stored within several different organelles including the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), ERGIC, the Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, and peroxisomes. A typical Ca2+ release pathway is shown at top: an extracellular ligand binds to its receptor, leading to production of IP3, which binds to the IP3R on the ER membrane, stimulating release of Ca2+ from the ER lumen. Note that the Golgi apparatus also contains IP3R molecules and thus may contribute to Ca2+ release from stores; Golgi Ca2+ uptake occurs via SPCA pumps. As shown at left, Ca2+ released from the ER has several different fates, including regulation of gene transcription within the nucleus; uptake by mitochondria, which are typically closely apposed to the ER network and where Ca2+ can affect metabolism; or extrusion from the cell via Na+/Ca2+ exchanger plasma membrane proteins. Peroxisomes are known to maintain Ca2+ at higher levels than those of the cytoplasm, but how this gradient is developed and maintained is not yet known. Ca2+ levels are elevated in the ER, in the SR, in the ERGIC, and in the Golgi apparatus, with most Ca2+ bound to buffering proteins, as shown within these organelles. The store-operated Ca2+ entry (SOC) is also represented. In response to depleted ER Ca2+ stores, an ER luminal Ca2+ sensor, STIM1, oligomerizes and migrates to subplasmalemmal punctae where it communicates with Orai1. Orai1 functions as a plasma membrane Ca2+ channel that allows for Ca2+ entry from the extracellular milieu into the cytoplasm, where it is taken up by SERCA into the ER lumen. BiP/GRP78 binding protein/glucose-regulated protein of 78-kDa; CRT, calreticulin; ERGIC, endoplasmic reticulum/Golgi intermediate complex; GRP94, glucose-regulated protein of 94-kDa; IP3, inositol trisphosphate; IP3R, inositol trisphosphate receptor; NCX, Na+/Ca2+ exchanger; P54/NEFA, DNA binding/EF hand/acidic amino acid rich region protein; PDI, protein disulfide isomerase; SERCA, sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase; SPCA, secretory pathway Ca2+-transport ATPase; STIM1, stromal interacting molecule 1.